A White-Box Machine Learning Approach for Revealing Antibiotic Mechanisms of Action
- PMID: 31080069
- PMCID: PMC6545570
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.04.016
A White-Box Machine Learning Approach for Revealing Antibiotic Mechanisms of Action
Abstract
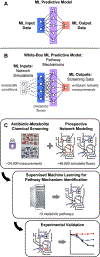
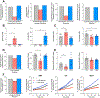
Current machine learning techniques enable robust association of biological signals with measured phenotypes, but these approaches are incapable of identifying causal relationships. Here, we develop an integrated "white-box" biochemical screening, network modeling, and machine learning approach for revealing causal mechanisms and apply this approach to understanding antibiotic efficacy. We counter-screen diverse metabolites against bactericidal antibiotics in Escherichia coli and simulate their corresponding metabolic states using a genome-scale metabolic network model. Regression of the measured screening data on model simulations reveals that purine biosynthesis participates in antibiotic lethality, which we validate experimentally. We show that antibiotic-induced adenine limitation increases ATP demand, which elevates central carbon metabolism activity and oxygen consumption, enhancing the killing effects of antibiotics. This work demonstrates how prospective network modeling can couple with machine learning to identify complex causal mechanisms underlying drug efficacy.
Keywords: ATP; LC-MS/MS; NADPH:NADP(+) ratio; adenylate energy charge; antibiotics; biochemical screen; machine learning; metabolism; network modeling; purine biosynthesis.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS
J.J.C. is scientific co-founder and scientific advisory board chair of Enbiotix, an antibiotics startup company.
Figures

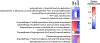

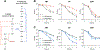

Comment in
-
Illuminating the dark side of machine learning.Nat Rev Genet. 2019 Jul;20(7):374-375. doi: 10.1038/s41576-019-0140-4. Nat Rev Genet. 2019. PMID: 31110256 No abstract available.
-
Antibiotic Lethality Is Impacted by Nutrient Availabilities: New Insights from Machine Learning.Cell. 2019 May 30;177(6):1373-1374. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.05.015. Cell. 2019. PMID: 31150617
References
-
- Andersen KB, and von Meyenburg K (1977). Charges of nicotinamide adenine nucleotides and adenylate energy charge as regulatory parameters of the metabolism in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 252, 4151–4156. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

