Overview of procalcitonin in pregnancy and in pre-eclampsia
- PMID: 31081935
- PMCID: PMC6718355
- DOI: 10.1111/cei.13311
Overview of procalcitonin in pregnancy and in pre-eclampsia
Abstract
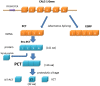
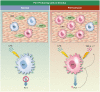
Procalcitonin (PCT), a precursor for calcitonin, is a prohormone involved in the inflammatory processes, which has been poorly studied in the context of pregnancy. During severe inflammation, PCT derives from almost all cell types, including monocytes and parenchymal tissues, making it a good predictive and diagnostic marker of an inflammatory state with rapidly increased serum levels in inflammation or sepsis. In normal pregnancy, PCT is basally expressed at very low level by decidual cells, even if decidual macrophages, which in normal pregnancy are skewed to M2 macrophages, are resistant to lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced production of PCT. As PCT increase is associated with an inflammatory state, several research groups investigated whether PCT can be considered a marker of pre-eclampsia, a pregnancy disease characterized by systemic inflammation. The first aim of this review is to summarize what is already known about the tissues synthesizing PCT, about the stimuli that cause the increase of circulating PCT levels and how PCT acts as a proinflammatory stimulus by itself. Secondly, we will describe the role of this prohormone in normal pregnancy and in pregnancies complicated by pre-eclampsia, highlighting the involvement of the decidual macrophages and the proinflammatory cytokine tumor necrosis factor-α in the modulation of PCT expression in the decidual microenvironment.
Keywords: TNF-α; macrophages; pre-eclampsia; pregnancy; procalcitonin.
© 2019 British Society for Immunology.
Conflict of interest statement
None to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Moya F, Nieto A, R‐candela JL. Calcitonin biosynthesis: evidence for a precursor. Eur J Biochem 1975; 55:407–13. - PubMed
-
- Meisner M. Pathobiochemistry and clinical use of procalcitonin. Clin Chim Acta 2002; 323:17‐29. - PubMed
-
- Matwiyoff GN, Prahl JD, Miller RJ et al Immune regulation of procalcitonin: a biomarker and mediator of infection. Inflamm Res 2012; 61:401–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

