Right anterior section graft for living-donor liver transplantation: A case report
- PMID: 31083154
- PMCID: PMC6531230
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000015212
Right anterior section graft for living-donor liver transplantation: A case report
Abstract
Rationale: In living-donor liver transplantation (LDLT), the right lobe graft is commonly utilized to prevent small-for-size syndrome, despite the considerable donor morbidity. Conversely, the feasibility of the left lobe graft and the right posterior section graft in smaller-sized recipients is now commonly employed with comparable outcomes to right lobe grafts. The efficacy of the right anterior section graft has rarely been reported.
Patient concerns: A 56-year-old man, a heavy alcoholic beverage drinker for 20 years, presented in the emergency department with massive ascites and lethargy. He was previously admitted twice due to bleeding esophageal varices.
Diagnosis: He was diagnosed with hepatic encephalopathy coma due to alcoholic liver cirrhosis. The Child-Turcotte-Pugh score was 11 (class C), and the Model for End-stage Liver Disease score was 21.62.
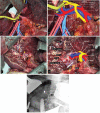
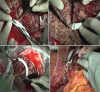
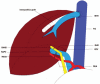
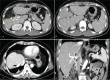
Intervention: A LDTL was offered to the patient as the best treatment option available. The patient's 26-year-old son was found to be the only donor-compatible candidate for the LDTL.Preoperatively, the right lobe of the donor occupied 76.2% of the total liver volume exposing the donor to a small residual liver volume. The right posterior section and left lobe volumes were insufficient, providing a graft-to-recipient weight ratio of 0.42% and 0.38%, respectively. However, the right anterior section could fulfill an acceptable GRWR of 0.83%. Thus, a living donor right anterior sectionectomy was performed.
Outcomes: Clinical signs and symptoms and liver function improved following anterior section graft transplantation without complications.
Lesson: The procurement of anterior section graft is technically feasible in selected patients, especially in high-volume liver centers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Hashikura Y, Makuuchi M, Kawasaki S, et al. Successful living-related partial liver transplantation to an adult patient. Lancet 1994;343:1233–4. - PubMed
-
- Chan SC, Fan ST, Lo CM, et al. A decade of right liver adult-to-adult living donor liver transplantation: the recipient mid-term outcomes. Ann Surg 2008;248:411–9. - PubMed
-
- Germani G, Theocharidou E, Adam R, et al. Liver transplantation for acute liver failure in Europe: outcomes over 20years from the ELTR database. J Hepatol 2012;57:288–96. - PubMed
-
- Moon DB, Lee SG, Hwang S, et al. More than 300 consecutive living donor liver transplants a year at a single center. Transplant Proc 2013;45:1942–7. - PubMed
-
- Beavers KL, Sandler RS, Shrestha R. Donor morbidity associated with right lobectomy for living donor liver transplantation to adult recipients: a systematic review. Liver Transpl 2002;8:110–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

