Elevated CTRP1 Plasma Concentration Is Associated with Sepsis and Pre-Existing Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Critically Ill Patients
- PMID: 31083558
- PMCID: PMC6572622
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm8050661
Elevated CTRP1 Plasma Concentration Is Associated with Sepsis and Pre-Existing Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Critically Ill Patients
Abstract
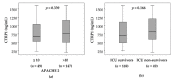
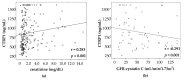
The adipokine family of C1q/TNF-like proteins (CTRP) plays a critical role in regulating systemic energy homeostasis and insulin sensitivity. It is involved in pathophysiological processes including inflammation and insulin-resistant obesity. Sepsis is associated with metabolic alterations and dysregulated adipokines, but the role of CTRP1 in critical illness and sepsis is unclear. We investigated CTRP1 plasma concentrations in 145 septic and 73 non-septic critically ill patients at admission to the medical intensive care unit (ICU) in comparison to 66 healthy controls. We also assessed associations of CTRP1 with clinical characteristics, adipokine levels, metabolic and inflammatory parameters. CTRP1 plasma concentration was significantly elevated in critically ill patients compared to healthy subjects. CTRP1 levels were significantly higher in ICU patients with sepsis. CTRP1 correlated strongly with markers of inflammatory response, renal function, liver damage and cholestasis. Furthermore, CTRP1 levels were higher in ICU patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, and correlated with HbA1c and body mass index. This study demonstrates significantly elevated levels of CTRP1 in critically ill patients, particularly with sepsis, and links circulating CTRP1 to inflammatory and metabolic disturbances.
Keywords: C1q/TNF-related protein 1; CTRP1; ICU; adipokine; critical illness; diabetes; glucose metabolism; inflammation; metabolism; sepsis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

