Enhancement of Hematoma Clearance With CD47 Blocking Antibody in Experimental Intracerebral Hemorrhage
- PMID: 31084334
- PMCID: PMC6538472
- DOI: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.118.024578
Enhancement of Hematoma Clearance With CD47 Blocking Antibody in Experimental Intracerebral Hemorrhage
Abstract
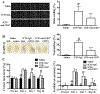
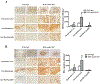
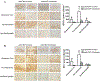
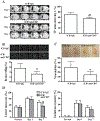
Background and Purpose- Our previous studies found that erythrocyte CD47 has a role in regulating hematoma resolution following experimental intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH). The current study examined whether or not a CD47 blocking antibody enhances hematoma clearance in a mouse ICH. Methods- ICH was induced by intracaudate injection of autologous blood in adult C57BL/6 mice. Mice had an ICH or ICH with CD47 blocking antibody or IgG coinjection. In subgroups of CD47 blocking antibody-treated mice, clodronate (to deplete microglia/macrophages) or control liposomes were coinjected. The effects of CD47 blocking antibody on ICH-induced brain injury were also tested in both males and females. Mice had magnetic resonance imaging to examine clot volume, iron deposition, brain swelling, and brain tissue loss. Behavioral tests were performed in all mice, and brains were harvested for brain immunohistochemistry. Results- In male mice, CD47 blocking antibody speeded up hematoma/iron clearance by macrophages/microglia and reduced ICH-induced brain swelling, neuronal loss, and neurological deficits. In contrast, clodronate liposome-induced microglia/macrophage depletion caused more severe brain swelling, neuronal loss, and functional deficits. In addition, similar injury severity in males and females was found in IgG control group and CD47 blocking antibody was also effective in females. Conclusions- Blocking CD47 in the hematoma speeded hematoma clearance and reduced brain injury after ICH suggesting it could be a treatment for ICH patients with surgical clot removal.
Keywords: cerebral hemorrhage; erythrocytes; macrophages; mice; microglia.
Figures


Comment in
-
Response by Hua et al to Letter Regarding Article, "Enhancement of Hematoma Clearance With CD47 Blocking Antibody in Experimental Intracerebral Hemorrhage".Stroke. 2019 Sep;50(9):e266. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.119.026620. Epub 2019 Jul 10. Stroke. 2019. PMID: 31288667 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Letter by Chen et al Regarding Article, "Enhancement of Hematoma Clearance With CD47 Blocking Antibody in Experimental Intracerebral Hemorrhage".Stroke. 2019 Sep;50(9):e265. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.119.026469. Epub 2019 Jul 10. Stroke. 2019. PMID: 31288668 No abstract available.
References
-
- Mebius RE, Kraal G. Structure and function of the spleen. Nature reviews. Immunology 2005;5:606–616 - PubMed
-
- Zhao X, Sun G, Zhang J, Strong R, Song W, Gonzales N, et al. Hematoma resolution as a target for intracerebral hemorrhage treatment: Role for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma in microglia/macrophages. Ann Neurol. 2007;61:352–362 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

