Digital Breast Tomosynthesis: Concepts and Clinical Practice
- PMID: 31084476
- PMCID: PMC6604796
- DOI: 10.1148/radiol.2019180760
Digital Breast Tomosynthesis: Concepts and Clinical Practice
Abstract
Digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) is emerging as the standard of care for breast imaging based on improvements in both screening and diagnostic imaging outcomes. The additional information obtained from the tomosynthesis acquisition decreases the confounding effect of overlapping tissue, allowing for improved lesion detection, characterization, and localization. In addition, the quasi three-dimensional information obtained from the reconstructed DBT data set allows a more efficient imaging work-up than imaging with two-dimensional full-field digital mammography alone. Herein, the authors review the benefits of DBT imaging in screening and diagnostic breast imaging.
© RSNA, 2019.
Figures




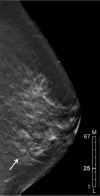

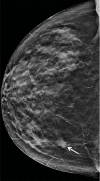

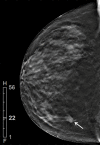

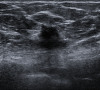











References
-
- Sechopoulos I, Ghetti C. Optimization of the acquisition geometry in digital tomosynthesis of the breast. Med Phys 2009;36(4):1199–1207. - PubMed
-
- Bissonnette M, Hansroul M, Masson E, et al. Digital breast tomosynthesis using an amorphous selenium flat panel detector. In: Flynn MJ, ed. Proceedings of SPIE: medical imaging 2005—physics of medical imaging. Vol 5745. Bellingham, Wash: International Society for Optics and Photonics, 2005; 529–540.
-
- Durand MA, Wang S, Hooley RJ, Raghu M, Philpotts LE. Tomosynthesis-detected architectural distortion: management algorithm with radiologic-pathologic correlation. RadioGraphics 2016;36(2):311–321. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

