Liposomes for effective drug delivery to the ocular posterior chamber
- PMID: 31084611
- PMCID: PMC6515668
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-019-0498-7
Liposomes for effective drug delivery to the ocular posterior chamber
Abstract
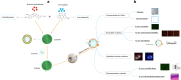
Background: Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a leading cause of severe visual deficits and blindness. Meanwhile, there is convincing evidence implicating oxidative stress, inflammation, and neovascularization in the onset and progression of AMD. Several studies have identified berberine hydrochloride and chrysophanol as potential treatments for ocular diseases based on their antioxidative, antiangiogenic, and anti-inflammatory effects. Unfortunately, their poor stability and bioavailability have limited their application. In order to overcome these disadvantages, we prepared a compound liposome system that can entrap these drugs simultaneously using the third polyamidoamine dendrimer (PAMAM G3.0) as a carrier.
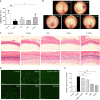
Results: PAMAM G3.0-coated compound liposomes exhibited appreciable cellular permeability in human corneal epithelial cells and enhanced bio-adhesion on rabbit corneal epithelium. Moreover, coated liposomes greatly improved BBH bioavailability. Further, coated liposomes exhibited obviously protective effects in human retinal pigment epithelial cells and rat retinas after photooxidative retinal injury. Finally, administration of P-CBLs showed no sign of side effects on ocular surface structure in rabbits model.
Conclusions: The PAMAM G3.0-liposome system thus displayed a potential use for treating various ocular diseases.
Keywords: Antioxidative retinal damage; Berberine hydrochloride; Chrysophanol; Ocular drug delivery; PAMAM G3.0-coated compound liposomes; Transcorneal permeability.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All animal experiments complied with the guidelines for animal use in ophthalmic and vision research. This study was approved by the Ethical Committee of Experimental Animal Care of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
[Corneal penetration of PAMAM dendrimers-coated puerarin liposomes].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2010 Jan;35(1):30-4. doi: 10.4268/cjcmm20100106. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2010. PMID: 20349711 Chinese.
-
Transcorneal iontophoresis of dendrimers: PAMAM corneal penetration and dexamethasone delivery.J Control Release. 2015 Feb 28;200:115-24. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2014.12.037. Epub 2014 Dec 29. J Control Release. 2015. PMID: 25553828
-
Fabrication and characterization of silk fibroin-coated liposomes for ocular drug delivery.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015 Apr;91:82-90. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2015.01.018. Epub 2015 Jan 31. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015. PMID: 25643990
-
Telomere Attrition in Human Lens Epithelial Cells Associated with Oxidative Stress Provide a New Therapeutic Target for the Treatment, Dissolving and Prevention of Cataract with N-Acetylcarnosine Lubricant Eye Drops. Kinetic, Pharmacological and Activity-Dependent Separation of Therapeutic Targeting: Transcorneal Penetration and Delivery of L-Carnosine in the Aqueous Humor and Hormone-Like Hypothalamic Antiaging Effects of the Instilled Ophthalmic Drug Through a Safe Eye Medication Technique.Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul. 2016;10(2):82-129. doi: 10.2174/1872211309666150618104657. Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul. 2016. PMID: 26084629 Review.
-
[Novel approach for management of age-related macular degeneration--antiangiogenic therapy and retinal regenerative therapy].Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2007 Mar;111(3):232-68; discussion 269. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2007. PMID: 17402564 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Nanomedicine Fight against Antibacterial Resistance: An Overview of the Recent Pharmaceutical Innovations.Pharmaceutics. 2020 Feb 8;12(2):142. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12020142. Pharmaceutics. 2020. PMID: 32046289 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Noble Metals and Soft Bio-Inspired Nanoparticles in Retinal Diseases Treatment: A Perspective.Cells. 2020 Mar 10;9(3):679. doi: 10.3390/cells9030679. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32164376 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combined Therapy of Experimental Autoimmune Uveitis by a Dual-Drug Nanocomposite Formulation with Berberine and Dexamethasone.Int J Nanomedicine. 2023 Jul 31;18:4347-4363. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S417750. eCollection 2023. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023. PMID: 37545873 Free PMC article.
-
Nanocarriers for the Delivery of Neuroprotective Agents in the Treatment of Ocular Neurodegenerative Diseases.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Mar 3;15(3):837. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15030837. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36986699 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overview of Recent Advances in Nano-Based Ocular Drug Delivery.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 19;24(20):15352. doi: 10.3390/ijms242015352. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37895032 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

