Independent amylase gene copy number bursts correlate with dietary preferences in mammals
- PMID: 31084707
- PMCID: PMC6516957
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.44628
Independent amylase gene copy number bursts correlate with dietary preferences in mammals
Abstract
The amylase gene (AMY), which codes for a starch-digesting enzyme in animals, underwent several gene copy number gains in humans (Perry et al., 2007), dogs (Axelsson et al., 2013), and mice (Schibler et al., 1982), possibly along with increased starch consumption during the evolution of these species. Here, we present comprehensive evidence for AMY copy number expansions that independently occurred in several mammalian species which consume diets rich in starch. We also provide correlative evidence that AMY gene duplications may be an essential first step for amylase to be expressed in saliva. Our findings underscore the overall importance of gene copy number amplification as a flexible and fast evolutionary mechanism that can independently occur in different branches of the phylogeny.
Keywords: adaptation; copy number variation; evolutionary biology; genetics; genomics; human; human commensalism; mouse; rat; rhesus macaque; saliva; starch; structural variation.
© 2019, Pajic et al.
Conflict of interest statement
PP, PP, KD, LN, RR, DG, ED, AG, SR, OG No competing interests declared
Figures


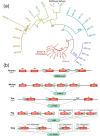
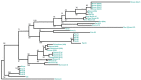

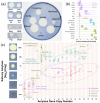



Comment in
-
Of starch and spit.Elife. 2019 May 14;8:e47523. doi: 10.7554/eLife.47523. Elife. 2019. PMID: 31084712 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ajayi SS. Field observations on the african giant rat Cricetomys gambianus waterhouse in southern Nigeria. African Journal of Ecology. 1977;15:191–198. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2028.1977.tb00397.x. - DOI
-
- Badan D. Diet of the house mouse (Mus musculus L.) in two pine and a kauri forest. New Zealand Journal of Ecology. 1986;9:137–142.
-
- Baker RH. Michigan Mammals. Michigan State University Press; 1991.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

