CHD4 is essential for transcriptional repression and lineage progression in B lymphopoiesis
- PMID: 31085655
- PMCID: PMC6561196
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1821301116
CHD4 is essential for transcriptional repression and lineage progression in B lymphopoiesis
Abstract
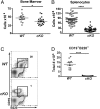
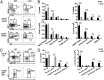
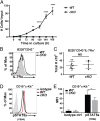
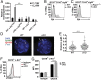
Cell lineage specification is a tightly regulated process that is dependent on appropriate expression of lineage and developmental stage-specific transcriptional programs. Here, we show that Chromodomain Helicase DNA-binding protein 4 (CHD4), a major ATPase/helicase subunit of Nucleosome Remodeling and Deacetylase Complexes (NuRD) in lymphocytes, is essential for specification of the early B cell lineage transcriptional program. In the absence of CHD4 in B cell progenitors in vivo, development of these cells is arrested at an early pro-B-like stage that is unresponsive to IL-7 receptor signaling and unable to efficiently complete V(D)J rearrangements at Igh loci. Our studies confirm that chromatin accessibility and transcription of thousands of gene loci are controlled dynamically by CHD4 during early B cell development. Strikingly, CHD4-deficient pro-B cells express transcripts of many non-B cell lineage genes, including genes that are characteristic of other hematopoietic lineages, neuronal cells, and the CNS, lung, pancreas, and other cell types. We conclude that CHD4 inhibits inappropriate transcription in pro-B cells. Together, our data demonstrate the importance of CHD4 in establishing and maintaining an appropriate transcriptome in early B lymphopoiesis via chromatin accessibility.
Keywords: B lymphocyte development; B lymphopoiesis; chromatin remodeling complexes; transcriptional programming; transcriptional repression.
Copyright © 2019 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Maier H, et al. (2004) Early B cell factor cooperates with Runx1 and mediates epigenetic changes associated with mb-1 transcription. Nat Immunol 5:1069–1077. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

