Adverse Health Outcomes in Relationship to Hypogonadism After Chemotherapy: A Multicenter Study of Testicular Cancer Survivors
- PMID: 31085753
- PMCID: PMC6712564
- DOI: 10.6004/jnccn.2018.7109
Adverse Health Outcomes in Relationship to Hypogonadism After Chemotherapy: A Multicenter Study of Testicular Cancer Survivors
Abstract
Background: This study examined the prevalence of hypogonadism, its clinical and genetic risk factors, and its relationship to adverse health outcomes (AHOs) in North American testicular cancer survivors (TCS) after modern platinum-based chemotherapy.
Patients and methods: Eligible TCS were <55 years of age at diagnosis and treated with first-line platinum-based chemotherapy. Participants underwent physical examinations and completed questionnaires regarding 15 AHOs and health behaviors. Hypogonadism was defined as serum testosterone levels ≤3.0 ng/mL or use of testosterone replacement therapy. We investigated the role of 2 single nucleotide polymorphisms (rs6258 and rs12150660) in the sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) locus implicated in increased hypogonadism risk in the general population.
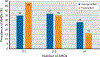
Results: Of 491 TCS (median age at assessment, 38.2 years; range, 18.7-68.4 years), 38.5% had hypogonadism. Multivariable binary logistic regression analysis identified hypogonadism risk factors, including age at clinical evaluation (odds ratio [OR], 1.42 per 10-year increase; P= .006) and body mass index of 25 to <30 kg/m2 (OR, 2.08; P= .011) or ≥30 kg/m2 (OR, 2.36; P= .005) compared with <25 kg/m2. TCS with ≥2 risk alleles for the SHBG SNPs had a marginally significant increased hypogonadism risk (OR, 1.45; P= .09). Vigorous-intensity physical activity appeared protective (OR, 0.66; P= .07). Type of cisplatin-based chemotherapy regimen and socioeconomic factors did not correlate with hypogonadism. Compared with TCS without hypogonadism, those with hypogonadism were more likely to report ≥2 AHOs (65% vs 51%; P= .003), to take medications for hypercholesterolemia (20.1% vs 6.0%; P<.001) or hypertension (18.5% vs 10.6%; P= .013), and to report erectile dysfunction (19.6% vs 11.9%; P= .018) or peripheral neuropathy (30.7% vs 22.5%; P= .041). A marginally significant trend for increased use of prescription medications for either diabetes (5.8% vs 2.6%; P= .07) or anxiety/depression (14.8% vs 9.3%; P= .06) was observed.
Conclusions: At a relatively young median age, more than one-third of TCS have hypogonadism, which is significantly associated with increased cardiovascular disease risk factors, and erectile dysfunction. Providers should screen TCS for hypogonadism and treat symptomatic patients.
Figures
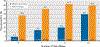
Comment in
-
Re: Adverse Health Outcomes in Relationship to Hypogonadism after Chemotherapy: A Multicenter Study of Testicular Cancer Survivors.J Urol. 2019 Dec;202(6):1081-1082. doi: 10.1097/01.JU.0000585196.65158.0d. Epub 2019 Sep 12. J Urol. 2019. PMID: 31512965 No abstract available.
References
-
- Nigam M, Aschebrook-Kilfoy B, Shikanov S, et al. Increasing incidence of testicular cancer in the United States and Europe between 1992 and 2009. World J Urol 2015;33:623–631. - PubMed
-
- Verdecchia A, Francisci S, Brenner H, et al. Recent cancer survival in Europe: a 2000–02 period analysis of EUROCARE-4 data. Lancet Oncol 2007;8:784–796. - PubMed
-
- Capocaccia R, Gatta G, Dal Maso L. Life expectancy of colon, breast, and testicular cancer patients: an analysis of US-SEER population-based data. Ann Oncol 2015;26:1263–1268. - PubMed
-
- Araujo AB, Esche GR, Kupelian V, et al. Prevalence of symptomatic androgen deficiency in men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2007;92:4241–247. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

