A per-protocol initiation of sacubitril/valsartan in an advanced heart failure disease management programme in the Middle East Gulf Region
- PMID: 31087629
- PMCID: PMC6676268
- DOI: 10.1002/ehf2.12452
A per-protocol initiation of sacubitril/valsartan in an advanced heart failure disease management programme in the Middle East Gulf Region
Abstract
Aims: The aim of this study is to evaluate the utilization and success in therapy intensification after initiation of sacubitril/valsartan using a specified protocol within an advanced heart failure and transplant programme in the Middle East Gulf Region.
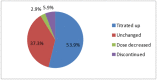
Methods and results: We studied a single-centre, retrospective cohort in a 364-bedded multi-speciality hospital located in the United Arab Emirates (February 2016 to July 2017). The advanced heart failure and transplant programme formulated an institutional protocol for initiation of sacubitril/valsartan with defined criteria for switching from angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor (ACEI) and angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB). Prescribing this drug is intended for patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction with left ventricular ejection fraction ≤40%. We excluded patients (i) with age below 18 years or (ii) initiated on sacubitril/valsartan from an outside hospital with or without follow-up in our outpatient clinic. We included 102 patients with an average initial dose of 78.9 ± 44.2 mg twice daily. Only 17 patients were on target doses of ACEI or ARB prior to switching to sacubitril/valsartan. Up-titration was successful in 55 patients during the follow-up period. In addition, 6.9% patients were hospitalized with heart failure exacerbation. In patients with elevated baseline serum potassium prior to initiating this medication, the serum potassium levels decreased post-initiation by 0.5 ± 0.3 mmol/L (P = 0.0008).
Conclusions: Initiating sacubitril/valsartan through a defined protocol selects for appropriate candidates and guides starting dose and titration. Overall, significant success can be achieved in replacing ACEI or ARB by sacubitril/valsartan in symptomatic heart failure with reduced ejection fraction patients.
Keywords: Angiotensin II and neprilysin inhibitor; Heart failure.
© 2019 The Authors. ESC Heart Failure published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
References
-
- McMurray JJ, Packer M, Desai AS, Gong J, Lefkowitz MP, Rizkala AR, Rouleau AL, Shi VC, Solomon SD, Swedberg K, Zile MR, PARADIGM‐HF Investigators and Committees . Angiotensin–neprilysin inhibition versus enalapril in heart failure. N Engl J Med 2014; 371: 993–1004. - PubMed
-
- Yancy CW, Jessup M, Bozkurt B, Butler J, Casey DE, Colvin MM, Drazner MH, Filippatos GS, Fonarow GC, Givertz MM, Hollenberg SM, Lindenfeld J, Masoudi FA, McBride PE, Peterson PN, Stevenson LW, Westlake C. 2017 ACC/AHA/HFSA focused update of the 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines and the Heart Failure Society of America. Circulation 2017; 136: e137–e161. - PubMed
-
- Vardeny O, Claggett B, Packer M, Zile MR, Rouleau J, Swedberg K, Teerlink JR, Desai AS, Lefkowitz M, Shi M, McMurray JJV, Solomon SD, Prospective Comparison of ARNI with ACEI to Determine Impact on Global Mortality and Morbidity in Heart Failure (PARADIGM‐HF) Investigators . Efficacy of sacubitril/valsartan vs. enalapril at lower than target doses in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: the PARADIGM‐HF trial. Eur J Heart Fail 2016; 18: 1228–1234. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Luo N, Fonarow GC, Lippmann SJ, Mi X, Heidenreich PA, Yancy CW, Greiner MA, Hammill BG, Hardy NC, Turner SJ, Laskey WK, Curtis LH, Hernandez AF, Mentz RJ, O'Brien EC. Early adoption of sacubitril/valsartan for patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: insights from Get with the Guidelines—Heart Failure (GWTG‐HF). JACC Heart Fail 2017; 5: 305–309. - PubMed
-
- Sulaiman K, Panduranga P, Al‐Zakwani I, Alsheikh‐Ali AA, AlHabib KF, Al‐Suwaidi J, Al‐Mahmeed W, AlFaleh H, Elasfar A, Al‐Motarreb A, Ridha M, Bulbanat B, Al‐Jarallah M, Bazargani N, Asaad N, Amin H. Clinical characteristic, management, and outcomes of acute heart failure patients: observations from the Gulf acute heart failure registry (Gulf CARE). Eur J Heart Fail 2015; 17: 374–384. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical