Brentuximab vedotin followed by bendamustine supercharge for refractory or relapsed Hodgkin lymphoma
- PMID: 31088808
- PMCID: PMC6517654
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2019000123
Brentuximab vedotin followed by bendamustine supercharge for refractory or relapsed Hodgkin lymphoma
Abstract
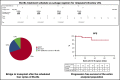
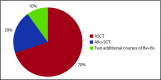
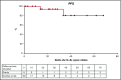
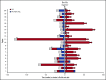
We evaluated the impact on progression-free survival (PFS) of achieving a deep metabolic response at 2-deoxy-2[18F] fluoro-d-glucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) in patients with refractory or relapsed (R/R) classic Hodgkin lymphoma (cHL) following a new salvage regimen named Bv+Bs (brentuximab vedotin + bendamustine supercharge), from 2013 to 2017. In this real-life study, 20 consecutive patients (aged <60 years) with R/R cHL after failure of ≥1 salvage treatments received Bv+Bs regimen consisting of 3-days outpatient IV infusions of 1.8 mg/kg of Bv on day 1 of each 3-week cycle combined in sequence to bendamustine on days 2 and 3 of the treatment cycle at a fixed dose of 120 mg/m2 per day, for a total of 4 courses. A robust primary prophylaxis approach, including premedication, antimicrobials, stimulating factors, and cytomegalovirus monitoring, was systematically performed. The 20 patients (all evaluable) underwent 4 courses of Bv+Bs with a median dose intensity of 100% for both Bv and Bs. Ten patients (50%) experienced grade ≥3 treatment-related adverse events, without requiring hospitalization. At post-Bv+Bs reevaluation, 80% of patients had deep metabolic responses with Deauville 5-point scale scores ≤2. Thereafter, 14 patients (70%) received autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT; peripheral blood stem cells previously harvested in 12 cases), and 4 patients (10%) received allogeneic HSCT. At a median follow-up of 27 months from Bv+Bs regimen initiation, the 2-year PFS of the entire population was 93.7% (95% confidence interval, 62.7% to 99.6%). Our data suggest that Bv+Bs regimen-driven strategy may be a promising salvage option to improve long-term control of high-risk Hodgkin lymphoma.
© 2019 by The American Society of Hematology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Kalac M, Lue JK, Lichtenstein E, et al. . Brentuximab vedotin and bendamustine produce high complete response rates in patients with chemotherapy refractory Hodgkin lymphoma. Br J Haematol. 2018;180(5):757-760. - PubMed
-
- Stefoni V, Casadei B, Botto B, et al. . The Bbv regimen: a phase II study with bendamustine plus brentuximab vedotin in Hodgkin lymphoma and CD30+ peripheral T-cell lymphoma in first salvage setting [abstract]. Blood. 2017;130(suppl 1). Abstract 4087.

