MicroRNA-126 regulates Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α which inhibited migration, proliferation, and angiogenesis in replicative endothelial senescence
- PMID: 31089163
- PMCID: PMC6517399
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-43689-3
MicroRNA-126 regulates Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α which inhibited migration, proliferation, and angiogenesis in replicative endothelial senescence
Abstract
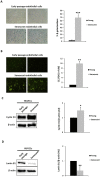
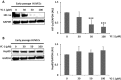
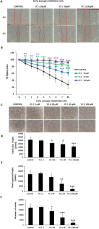
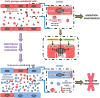
Whereas a healthy endothelium maintains physiological vascular functions, endothelial damage contributes to the development of cardiovascular diseases. Endothelial senescence is the main determinant of endothelial dysfunction and thus of age-related cardiovascular disease. The objective of this study is to test the involvement of microRNA-126 and HIF-1α in a model of replicative endothelial senescence and the interrelationship between both molecules in this in vitro model. We demonstrated that senescent endothelial cells experience impaired tube formation and delayed wound healing. Senescent endothelial cells failed to express HIF-1α, and the microvesicles released by these cells failed to carry HIF-1α. Of note, HIF-1α protein levels were restored in HIF-1α stabilizer-treated senescent endothelial cells. Finally, we show that microRNA-126 was downregulated in senescent endothelial cells and microvesicles. With regard to the interplay between microRNA-126 and HIF-1α, transfection with a microRNA-126 inhibitor downregulated HIF-1α expression in early passage endothelial cells. Moreover, while HIF-1α inhibition reduced tube formation and wound healing closure, microRNA-126 levels remained unchanged. These data indicate that HIF-1α is a target of miRNA-126 in protective and reparative functions, and suggest that their therapeutic modulation could benefit age-related vascular disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Carrecedo J, R.-C. R., Alique M. & Ramírez-Chamond R. Endothelial cell senescence in the pathogenesis of endothelial dysfunction. 1–16 (Intech, 2018).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K23HL111339/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)/International
- R03HL135289/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)/International
- R21TR001739/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS)/International
- UH2TR002067/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS)/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

