Immuno-Imaging to Predict Treatment Response in Infection, Inflammation and Oncology
- PMID: 31091813
- PMCID: PMC6571748
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm8050681
Immuno-Imaging to Predict Treatment Response in Infection, Inflammation and Oncology
Abstract
Background: Molecular nuclear medicine plays a pivotal role for diagnosis in a preclinical phase, in genetically susceptible patients, for radio-guided surgery, for disease relapse evaluation, and for therapy decision-making and follow-up. This is possible thanks to the development of new radiopharmaceuticals to target specific biomarkers of infection, inflammation and tumour immunology.
Methods: In this review, we describe the use of specific radiopharmaceuticals for infectious and inflammatory diseases with the aim of fast and accurate diagnosis and treatment follow-up. Furthermore, we focus on specific oncological indications with an emphasis on tumour immunology and visualizing the tumour environment.
Results: Molecular nuclear medicine imaging techniques get a foothold in the diagnosis of a variety of infectious and inflammatory diseases, such as bacterial and fungal infections, rheumatoid arthritis, and large vessel vasculitis, but also for treatment response in cancer immunotherapy.
Conclusion: Several specific radiopharmaceuticals can be used to improve diagnosis and staging, but also for therapy decision-making and follow-up in infectious, inflammatory and oncological diseases where immune cells are involved. The identification of these cell subpopulations by nuclear medicine techniques would provide personalized medicine for these patients, avoiding side effects and improving therapeutic approaches.
Keywords: infection; inflammation; personalised medicine; therapy follow-up; tumour immunology; tumour microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

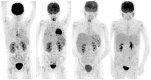
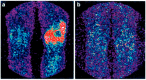
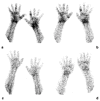
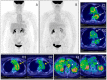
References
-
- Glaudemans A.W., Prandini N., Di Girolamo M., Argento G., Lauri C., Lazzeri E., Muto M., Sconfienza L.M., Signore A. Hybrid imaging of musculoskeletal infections. Q. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging. 2018;62:3–13. - PubMed
-
- Ruf J., Oeser C., Amthauer H. Clinical role of anti-granulocyte MoAb versus radiolabeled white blood cells. Q. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging. 2010;54:599–616. - PubMed
-
- Malherbe C., Dupont A.C., Maia S., Venel Y., Erra B., Santiago-Ribeiro M.J., Arlicot N. Estimation of the added value of 99mTc-HMPAO labelled white blood cells scintigraphy for the diagnosis of infectious foci. Q. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging. 2017;61 doi: 10.23736/S1824-4785.17.02964-8. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

