Monitoring dynamic cytotoxic chemotherapy response in castration-resistant prostate cancer using plasma cell-free DNA (cfDNA)
- PMID: 31092276
- PMCID: PMC6521434
- DOI: 10.1186/s13104-019-4312-2
Monitoring dynamic cytotoxic chemotherapy response in castration-resistant prostate cancer using plasma cell-free DNA (cfDNA)
Abstract
Objective: Cell-free DNA (cfDNA) is an attractive cancer biomarker, as it is thought to reflect a component of the underlying genetic makeup of the tumor and is readily accessible in serial fashion. Because chemotherapy regimens are expected to act rapidly on cancer and cfDNA is cleared from the blood within minutes, we hypothesized that cfDNA would reflect immediate effects of treatment. Here, we developed a method for monitoring long cfDNA fragments, and report dynamic changes in response to cytotoxic chemotherapy.
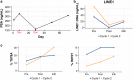
Results: Peripheral blood was obtained from 15 patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) immediately before and after cytotoxic chemotherapy infusion. cfDNA was extracted and quantified for long interspersed nuclear elements (LINE1; 297 bp) using qPCR. Targeted deep sequencing was performed to quantify the frequency of mutations in exon 8 of the androgen receptor (AR), a mutational hotspot region in CRPC. Single nucleotide mutations in AR exon 8 were found in 6 subjects (6/15 = 40%). Analytical variability was minimized by pooling independent PCR reactions for each library. In 5 patients, tumor-derived long cfDNA levels were found to change immediately after infusion. Detailed analysis of one subject suggests that cytotoxic chemotherapy can produce rapidly observable effects on cfDNA.
Keywords: Androgen receptor; Cell-free DNA; Chemotherapy; Prostate cancer; Sequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Ethical approval and oversight for prospective sample collection was performed with the consent of all research subjects under auspices of the University of Southern California Institutional Review Board (IRB Protocol number: HS-11-00450). Prospective, voluntary written informed consent was obtained from all subjects prior to data and specimen collection.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Handy CE, Antonarakis ES. Sequencing treatment for castration-resistant prostate cancer. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2016;17(12):64. - PubMed
-
- Taplin ME, Bubley GJ, Ko YJ, Small EJ, Upton M, Rajeshkumar B. Selection for androgen receptor mutations in prostate cancers treated with androgen antagonist. Cancer Res. 1999;59(11):2511–2515. - PubMed
-
- Taplin ME, Bubley GJ, Shuster TD, Frantz ME, Spooner AE, Ogata GK. Mutation of the androgen-receptor gene in metastatic androgen-independent prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 1995;332(21):1393–1398. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

