HIV, syphilis, and viral hepatitis among Latin American indigenous peoples and Afro-descendants: a systematic review
- PMID: 31093241
- PMCID: PMC6393722
- DOI: 10.26633/RPSP.2019.17
HIV, syphilis, and viral hepatitis among Latin American indigenous peoples and Afro-descendants: a systematic review
Abstract
Objective: To identify and summarize existing literature on the burden of HIV, sexually transmitted infections (STIs), and viral hepatitis (VH) in indigenous peoples and Afro-descendants in Latin America to provide a broad panorama of the quantitative data available and highlight problematic data gaps.
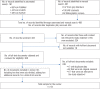
Methods: Published and grey literature were systematically reviewed to identify documents published in English, Spanish, or Portuguese with data collected between January 2000 and April 2016 on HIV, STI, and VH disease burden among indigenous peoples and Afro-descendants in 17 Latin American countries.
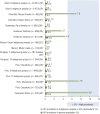
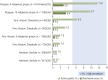
Results: Sixty-two documents from 12 countries were found. HIV prevalence was generally low (< 1%) but pockets of high prevalence (> 5%) were noted in some indigenous communities in Venezuela (Warao) (9.6%), Peru (Chayahuita) (7.5%), and Colombia (Wayuu females) (7.0%). High active syphilis prevalence (> 5%) was seen in some indigenous communities in Paraguay (11.6% and 9.7%) and Peru (Chayahuita) (6.3%). High endemicity (> 8%) of hepatitis B was found in some indigenous peoples in Mexico (Huichol) (9.4%) and Venezuela (Yanomami: 14.3%; Japreira: 29.5%) and among Afro-descendant quilombola populations in Brazil (Frechal: 12.5%; Furnas do Dionísio: 8.4% in 2008, 9.2% in 2003).
Conclusions: The gaps in existing data on the burden of HIV, STIs, and VH in indigenous peoples and Afro-descendants in Latin America highlight the need to 1) improve national surveillance, by systematically collecting and analyzing ethnicity variables, and implementing integrated biobehavioral studies using robust methodologies and culturally sensitive strategies; 2) develop a region-wide response policy that considers the needs of indigenous peoples and Afro-descendants; and 3) implement an intercultural approach to health and service delivery to eliminate health access barriers and improve health outcomes for these populations.
Objetivo: Identificar y resumir la bibliografía existente sobre la carga de la infección por el VIH, las infecciones de transmisión sexual (ITS) y las hepatitis virales en las poblaciones indígenas y afrodescendientes en América Latina para proporcionar un panorama amplio de los datos cuantitativos disponibles y poner de relieve las brechas problemáticas que pudiera haber en los datos.
Métodos: Se hizo un examen sistemático de la bibliografía publicada y la bibliografía gris para encontrar documentos publicados en inglés, español o portugués con datos recogidos entre enero del 2000 y abril del 2016 sobre la carga de la infección por el VIH, las ITS y las hepatitis virales en las poblaciones indígenas y afrodescendientes en 17 países latinoamericanos.
Resultados: Se encontraron 62 documentos de 12 países. La prevalencia de la infección por el VIH fue generalmente baja (< 1%), pero se observaron focos de prevalencia alta (> 5%) en algunas comunidades indígenas en Venezuela (Warao) (9,6%), Perú (Chayahuita) (7,5%) y Colombia (las mujeres Wayuus) (7,0%). Se observó prevalencia alta de sífilis activa (> 5%) en algunas comunidades indígenas en Paraguay (11,6% y 9,7%) y Perú (Chayahuita) (6,3%). Se encontró endemicidad alta (> 8%) de la hepatitis B en algunos pueblos indígenas en México (Huichol) (9,4%) y Venezuela (Yanomami: 14,3%; Japreira: 29,5%) y en las poblaciones quilombola de afrodescendientes en Brasil (Frechal: 12,5%; Furnas do Dionísio: 8,4% en el 2008, 9,2% en el 2003).
Conclusiones: Las brechas en los datos existentes sobre la carga de la infección por el VIH, las ITS y las hepatitis virales en las poblaciones indígenas y afrodescendientes en América Latina destacan la necesidad de: 1) mejorar la vigilancia nacional mediante la recolección y el análisis sistemáticos de las variables de etnicidad y la ejecución de estudios bioconductuales integrados que utilicen metodologías sólidas y estrategias sensibles a diferencias entre las culturas; 2) elaborar una política de respuesta de alcance regional que considere las necesidades de las poblaciones indígenas y de afrodescendientes; y 3) aplicar un enfoque intercultural de la salud y de la prestación de servicios conexos para eliminar las barreras de acceso a la salud y mejorar los resultados en materia de salud para estas poblaciones.
Objetivo: Identificar e sintetizar a literatura existente sobre a carga de HIV, infecções sexualmente transmissíveis (IST) e hepatite viral nos povos indígenas e afrodescendentes da América Latina para traçar um amplo panorama dos dados quantitativos disponíveis e destacar as lacunas problemáticas nos dados.
Métodos: Foi realizada uma revisão sistemática da literatura publicada e da literatura cinzenta para identificar documentos publicados em inglês, espanhol ou português com dados coletados entre janeiro de 2000 e abril de 2016 sobre a carga de HIV, IST e hepatite viral nos povos indígenas e afrodescendentes em 17 países latino-americanos.
Resultados: Sessenta e dois documentos de 12 países foram encontrados. A prevalência de HIV observada foi em geral baixa (<1%), com focos de alta prevalência (>5%) observados em comunidades indígenas da Venezuela (warao) (9,6%), Peru (chayahuita) (7,5%) e Colômbia (mulheres wayúu) (7,0%). Foi verificada uma alta prevalência de sífilis ativa (> 5%) em comunidades indígenas no Paraguai (11,6% e 9,7%) e Peru (chayahuita) (6,3%). A alta endemicidade (>8%) de hepatite B foi observada em povos indígenas no México (huichol) (9,4%) e Venezuela (ianomâmi 14,3%; japrería 29,5%) e em comunidades negras quilombolas no Brasil (Frechal 12,5%; Furnas do Dionísio 8,4% em 2008 e 9,2% em 2003).
Conclusões: As lacunas nos dados existentes sobre a carga de HIV, IST e hepatite viral nos povos indígenas e afrodescendentes na América Latina destacam a necessidade de: melhorar a vigilância nacional com coleta sistemática e análise de variáveis de etnicidade e realizar estudos integrados de análise biocomportamental com o uso de metodologias robustas e estratégias sensíveis à diversidade cultural; desenvolver uma política de resposta regional que considere as necessidades dos povos indígenas e afrodescendentes; e implementar um enfoque intercultural à saúde e prestação de serviços para derrubar as barreiras de acesso à saúde e melhorar os resultados de saúde nestas populações.
Keywords: HIV; Latin America; health of indigenous peoples; hepatitis, viral, human; sexually transmitted diseases; syphilis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest. None.
Figures

References
-
- United Nations General Assembly Political declaration on HIV and AIDS: on the fast-track to accelerate the fight against HIV and to end the AIDS epidemic by 2030. 70th Session, Agenda Item 11. 2016 Jun 8. Points 62j, 64a. (A/Res/70266) Available from: http://www.unaids.org/sites/default/files/media_asset/2016-political-dec....
-
- Minichiello V, Rahman S, Hussain R. Epidemiology of sexually transmitted infections in global indigenous populations: data availability and gaps. Int J STD AIDS. 2013;24(10):759–768. - PubMed
-
- De Carvalho NS, Cho R, Flores LP. DST em populações indígenas no Brasil – análise crítica e revisão da literatura DST. J Bras Doenças Sex Transm. 2011;23(3):142–145.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
