Evaluation of the Antinociceptive Effect of Maropitant, a Neurokinin-1 Receptor Antagonist, in Cats Undergoing Ovariohysterectomy
- PMID: 31093325
- PMCID: PMC6476118
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/9352528
Evaluation of the Antinociceptive Effect of Maropitant, a Neurokinin-1 Receptor Antagonist, in Cats Undergoing Ovariohysterectomy
Abstract
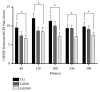
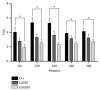
Maropitant is a neurokinin-1 (NK1) receptor antagonist that can be used for pain management. The objective of this study was to evaluate the effect of continuous infusion of two doses of maropitant on cardiorespiratory parameters and its postoperative analgesic effect in cats undergoing ovariohysterectomy. Thirty cats were randomly assigned to one of three groups (10 cats each group): the control group (CG) received a continuous infusion of 10 ml/kg/h Ringer's lactate; GM30 and GM100 first received an intravenous (IV) bolus of 1 mg/kg maropitant; GM30 then received continuous infusion of 30 μg/kg/h maropitant; and GM100 then received continuous infusion of 100 μg/kg/h maropitant. The maropitant was diluted into Ringer's lactate and the GM30 and GM100 also received fluids intraoperatively. In all groups, premedication included intramuscular injections of morphine and acepromazine, followed by induction with propofol and maintenance with isoflurane. Temperature, heart rate (HR), Doppler blood pressure (DBP), respiratory rate, oxygen saturation, and measuring the end-tidal carbon dioxide and isoflurane were monitored. Postoperative pain was evaluated using a visual analog scale and the UNESP-Botucatu multidimensional composite pain scale in cats; morphine was used for analgesic rescue. During the surgical procedure, cats in GM100 demonstrated lower HR and DBP than those in CG. With regard to the evaluation of postoperative pain, GM100 required the least frequent morphine rescue and less rescue analgesia compared with CG. In conclusion, cats in GM100 maintained lower DBP and HR and required lower analgesic rescue during the postoperative period. The results suggested that animals receiving maropitant bolus (1 mg/kg) plus (100 μg/kg/h) experienced greater postoperative comfort, reflected by the lesser need for analgesic rescue. The use of maropitant in surgical procedures in cats contributes to postoperative comfort.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antinociceptive and analgesic effect of continuous intravenous infusion of maropitant, lidocaine and ketamine alone or in combination in cats undergoing ovariohysterectomy.Acta Vet Scand. 2021 Nov 27;63(1):49. doi: 10.1186/s13028-021-00615-w. Acta Vet Scand. 2021. PMID: 34838084 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of analgesic interaction between morphine, maropitant and dexmedetomidine in dogs undergoing ovariohysterectomy.N Z Vet J. 2022 Jan;70(1):10-21. doi: 10.1080/00480169.2021.1927231. Epub 2021 Jun 9. N Z Vet J. 2022. PMID: 33950785
-
Comparison of NK-1 Receptor Antagonist (Maropitant) to Morphine as a Pre-Anaesthetic Agent for Canine Ovariohysterectomy.PLoS One. 2015 Oct 29;10(10):e0140734. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0140734. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26513745 Free PMC article.
-
Spotlight on the perioperative use of maropitant citrate.Vet Med (Auckl). 2017 Aug 24;8:41-51. doi: 10.2147/VMRR.S126469. eCollection 2017. Vet Med (Auckl). 2017. PMID: 30050855 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluating the anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties of maropitant: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Vet J. 2020 May-Jun;259-260:105471. doi: 10.1016/j.tvjl.2020.105471. Epub 2020 May 17. Vet J. 2020. PMID: 32553233
Cited by
-
Antinociceptive and analgesic effect of continuous intravenous infusion of maropitant, lidocaine and ketamine alone or in combination in cats undergoing ovariohysterectomy.Acta Vet Scand. 2021 Nov 27;63(1):49. doi: 10.1186/s13028-021-00615-w. Acta Vet Scand. 2021. PMID: 34838084 Free PMC article.
-
Post-treatment with maropitant reduces oxidative stress, endoplasmic reticulum stress and neuroinflammation on peripheral nerve injury in rats.PLoS One. 2024 Mar 20;19(3):e0287390. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0287390. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38507417 Free PMC article.
-
Continuous Infusion of Ketamine and Lidocaine Either with or without Maropitant as an Adjuvant Agent for Analgesia in Female Dogs Undergoing Mastectomy.Vet Med Int. 2021 Jan 26;2021:4747301. doi: 10.1155/2021/4747301. eCollection 2021. Vet Med Int. 2021. PMID: 33575023 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of intravenous maropitant on blood pressure in healthy awake and anesthetized dogs.PLoS One. 2020 Feb 27;15(2):e0229736. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0229736. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32108177 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Maropitant, Ondansetron and Metoclopramide on Dexmedetomidine-Induced Vomiting in Cats.Vet Med Sci. 2025 Jan;11(1):e70152. doi: 10.1002/vms3.70152. Vet Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 39792081 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boscan P., Monnet E., Mama K., Twedt D. C., Congdon J., Steffey E. P. Effect of maropitant, a neurokinin 1 receptor antagonist, on anesthetic requirements during noxious visceral stimulation of the ovary in dogs. American Journal of Veterinary Research. 2011;72(12):1576–1579. doi: 10.2460/ajvr.72.12.1576. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Niyom S., Boscan P., Twedt D. C., Monnet E., Eickhoff J. C. Effect of maropitant, a neurokinin-1 receptor antagonist, on the minimum alveolar concentration of sevoflurane during stimulation of the ovarian ligament in cats. Veterinary Anaesthesia and Analgesia. 2013;40(4):425–431. doi: 10.1111/vaa.12017. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

