Tufts PACE Clinical Predictive Model Registry: update 1990 through 2015
- PMID: 31093549
- PMCID: PMC6460840
- DOI: 10.1186/s41512-017-0021-2
Tufts PACE Clinical Predictive Model Registry: update 1990 through 2015
Abstract
Background: Clinical predictive models (CPMs) estimate the probability of clinical outcomes and hold the potential to improve decision-making and individualize care. The Tufts Predictive Analytics and Comparative Effectiveness (PACE) CPM Registry is a comprehensive database of cardiovascular disease (CVD) CPMs. The Registry was last updated in 2012, and there continues to be substantial growth in the number of available CPMs.
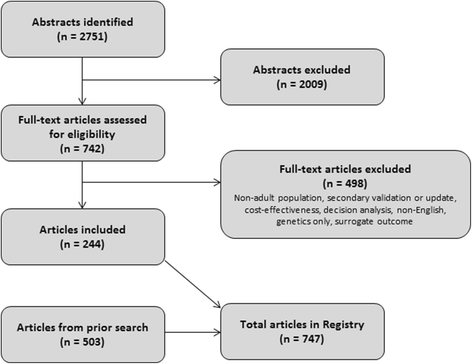
Methods: We updated a systematic review of CPMs for CVD to include articles published from January 1990 to March 2015. CVD includes coronary artery disease (CAD), congestive heart failure (CHF), arrhythmias, stroke, venous thromboembolism (VTE), and peripheral vascular disease (PVD). The updated Registry characterizes CPMs based on population under study, model performance, covariates, and predicted outcomes.
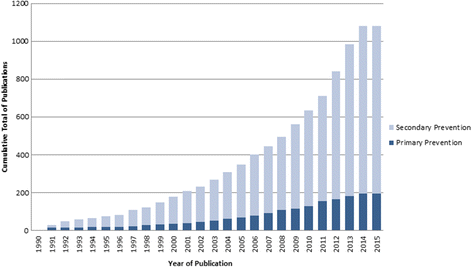
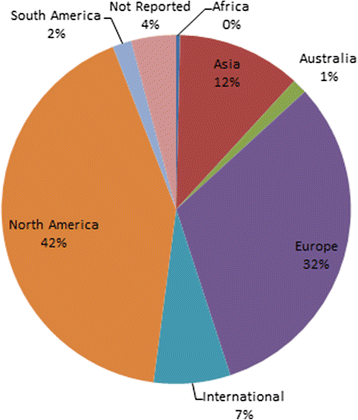
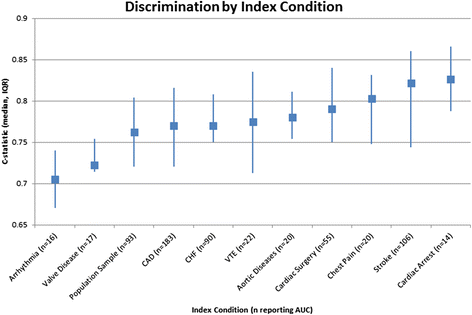
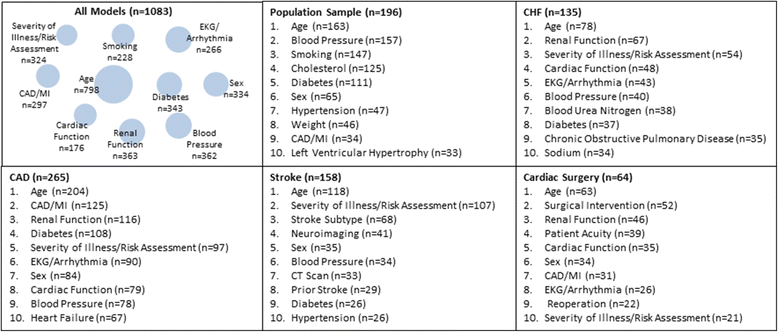
Results: The Registry includes 747 articles presenting 1083 models, including both prognostic (n = 1060) and diagnostic (n = 23) CPMs representing 183 distinct index condition/outcome pairs. There was a threefold increase in the number of CPMs published between 2005 and 2014, compared to the prior 10-year interval from 1995 to 2004. The majority of CPMs were derived from either North American (n = 455, 42%) or European (n = 344, 32%) populations. The database contains 265 CPMs predicting outcomes for patients with coronary artery disease, 196 CPMs for population samples at risk for incident CVD, and 158 models for patients with stroke. Approximately two thirds (n = 701, 65%) of CPMs report a c-statistic, with a median reported c-statistic of 0.77 (IQR, 0.05). Of the CPMs reporting validations, only 333 (57%) report some measure of model calibration. Reporting of discrimination but not calibration is improving over time (p for trend < 0.0001 and 0.39 respectively).
Conclusions: There is substantial redundancy of CPMs for a wide spectrum of CVD conditions. While the number of CPMs continues to increase, model performance is often inadequately reported and calibration is infrequently assessed. More work is needed to understand the potential impact of this literature.
Keywords: Cardiovascular disease risk factors; Cerebrovascular disease/stroke; Clinical predictive model; Coronary artery disease; Methods; Modeling; Prediction; Prognostic factor; Risk stratification.
Conflict of interest statement
Not applicable.Not applicable.The authors declare that they have no competing interests.Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Stone NJ, Robinson JG, Lichtenstein AH, Bairey Merz CN, Blum CB, Eckel RH, Goldberg AC, Gordon D, Levy D, Lloyd-Jones DM, McBride P, Schwartz JS, Shero ST, Smith SC, Watson K, Wilson PWF. 2013 ACC/AHA guideline on the treatment of blood cholesterol to reduce atherosclerotic cardiovascular risk in adults: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on practice guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;63:2889–2934. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.11.002. - DOI - PubMed
-
- January CT, Wann LS, Alpert JS, Calkins H, Cleveland JC, Cigarroa JE, Conti JB, Ellinor PT, Ezekowitz MD, Field ME, Murray KT, Sacco RL, Stevenson WG, Tchou PJ, Tracy CM, Yancy CW, Cleveland JC, Conti JB, Ellinor PT, Ezekowitz MD, Field ME, Murray KT, Sacco RL, Stevenson WG, Tchou PJ, Tracy CM, Yancy CW. 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS guideline for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on practice guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;64:e1–e76. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2014.03.022. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yancy CW, Jessup M, Bozkurt B, Butler J, Casey DE, Drazner MH, Fonarow GC, Geraci SA, Horwich T, Januzzi JL, Johnson MR, Kasper EK, Levy WC, Masoudi FA, McBride PE, McMurray JJV, Mitchell JE, Peterson PN, Riegel B, Sam F, Stevenson LW, Tang WHW, Tsai EJ, Wilkoff BL. 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on practice guidelines. Circulation. 2013;128:e240–e327. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0b013e31829e8807. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
