Music training with Démos program positively influences cognitive functions in children from low socio-economic backgrounds
- PMID: 31095606
- PMCID: PMC6522123
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0216874
Music training with Démos program positively influences cognitive functions in children from low socio-economic backgrounds
Abstract
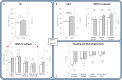
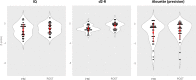
This study aimed at evaluating the impact of a classic music training program (Démos) on several aspects of the cognitive development of children from low socio-economic backgrounds. We were specifically interested in general intelligence, phonological awareness and reading abilities, and in other cognitive abilities that may be improved by music training such as auditory and visual attention, working and short-term memory and visuomotor precision. We used a longitudinal approach with children presented with standardized tests before the start and after 18 months of music training. To test for pre-to-post training improvements while discarding maturation and developmental effects, raw scores for each child and for each test were normalized relative to their age group. Results showed that Démos music training improved musicality scores, total IQ and Symbol Search scores as well as concentration abilities and reading precision. In line with previous results, these findings demonstrate the positive impact of an ecologically-valid music training program on the cognitive development of children from low socio-economic backgrounds and strongly encourage the broader implementation of such programs in disadvantaged school-settings.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Schellenberg EG. Long-term positive associations between music lessons and IQ. Journal of Educational Psychology. 2006;98(2):457–68.
-
- Sala G, Gobet F. When the music’s over. Does music skill transfer to children’s and young adolescents’ cognitive and academic skills? A meta-analysis. Educational Research Review. 2017;20:55–67.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

