Effectiveness of dienogest in improving quality of life in Asian women with endometriosis (ENVISIOeN): interim results from a prospective cohort study under real-life clinical practice
- PMID: 31096979
- PMCID: PMC6524261
- DOI: 10.1186/s12905-019-0758-6
Effectiveness of dienogest in improving quality of life in Asian women with endometriosis (ENVISIOeN): interim results from a prospective cohort study under real-life clinical practice
Abstract
Background: Dienogest has been shown to substantially improve endometriosis-associated symptoms such as debilitating chronic pelvic pain, and in turn, health-related quality of life (HRQoL). To date, there is no data on patient-reported outcomes reflecting the real-world practice in Asia where endometriosis is a relevant health, social and economic burden. This non-interventional, multi-center, prospective study aims to investigate the influence of dienogest on HRQoL.
Methods: Asian women received dienogest (2 mg/daily) and were followed for 24 months. The effectiveness of dienogest to improve HRQoL and endometriosis-associated pelvic pain (EAPP) was assessed by patient-reported outcomes. HRQoL, especially the "pain" domain as primary endpoint, was evaluated with the Endometriosis Health Profile-30 (EHP-30) questionnaire. The numeric rating scale served to determine changes in the severity of EAPP. Within the presented interim analysis (data cut-off: 2017-11-27), the mean changes in EHP-30 and EAPP scores from baseline to 6 months upon availability of the data were evaluated. Treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) and bleeding profiles were documented.
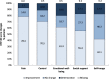
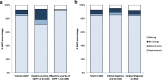
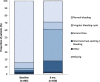
Results: Dienogest therapy decreased EHP-30 scores in all assessed domains (score 0-100, lower scores indicate better HRQoL). Primarily, the "pain" domain was improved in 78.4% of patients. EAPP was reduced (score 0-10, lower scores reflect less pain), highlighted by a mean reduction of the pain score by - 4.5 points. Patients with a higher EAPP score at baseline had an increased response to dienogest (- 6.2 points mean change) compared to patients with low baseline EAPP severity (- 1.4 points mean change). Both surgically and clinically diagnosed patients described comparable pain reduction, as well as women with or without prior treatment. Drug-related TEAEs were documented for 31.5% of patients, with amenorrhoea (5.9%) and metrorrhagia (5.1%) being the most common events. The bleeding pattern was changed upon dienogest, characterized by decreased normal bleeding (84.2 to 28.8%) and increased amenorrhea (3.2 to 42.9%) at 6 months.
Conclusion: The data indicate an amelioration of HRQoL and EAPP upon dienogest therapy. No new safety signals were observed. Therefore, its use as first-line therapy for long-term management of debilitating and chronic endometriosis-associated pain represents an interesting option that remains to be further investigated.
Trial registration: Name of registry: Clinical Trials Clinicaltrials.gov registration number: NCT02425462 Registration date: 2015-04-24. Registration timing: prospective.
Keywords: Asian women; Clinical diagnosis; Endometriosis; Health-related quality of life; Pain.
Conflict of interest statement
CA is a current employee of Bayer AG, Berlin, Germany and SS is a former employee of Bayer AG. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of Long-Term Dienogest Therapy on Quality of Life in Asian Women with Endometriosis: the Prospective Non-Interventional Study ENVISIOeN.Reprod Sci. 2022 Apr;29(4):1157-1169. doi: 10.1007/s43032-021-00787-w. Epub 2022 Feb 2. Reprod Sci. 2022. PMID: 35112299 Free PMC article.
-
Dienogest for Treatment of Endometriosis in Women: A 28-Week, Open-Label, Extension Study.J Womens Health (Larchmt). 2019 Feb;28(2):170-177. doi: 10.1089/jwh.2018.7084. Epub 2018 Nov 21. J Womens Health (Larchmt). 2019. PMID: 30461337 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy of dienogest vs combined oral contraceptive on pain associated with endometriosis: Randomized clinical trial.Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2021 Dec;267:205-212. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2021.10.029. Epub 2021 Oct 30. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2021. PMID: 34826668 Clinical Trial.
-
Use of dienogest in endometriosis: a narrative literature review and expert commentary.Curr Med Res Opin. 2020 May;36(5):895-907. doi: 10.1080/03007995.2020.1744120. Epub 2020 Mar 31. Curr Med Res Opin. 2020. PMID: 32175777 Review.
-
[New medical treatments for painful endometriosis: CNGOF-HAS Endometriosis Guidelines].Gynecol Obstet Fertil Senol. 2018 Mar;46(3):256-263. doi: 10.1016/j.gofs.2018.02.009. Epub 2018 Mar 9. Gynecol Obstet Fertil Senol. 2018. PMID: 29530558 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Hormonal treatments for endometriosis: The endocrine background.Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2022 Jun;23(3):333-355. doi: 10.1007/s11154-021-09666-w. Epub 2021 Aug 17. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2022. PMID: 34405378 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical Efficacy of Dienogest versus Levonorgestrel-Releasing Intrauterine System for Adenomyosis.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Jul 15;2022:1995472. doi: 10.1155/2022/1995472. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. Retraction in: Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023 Jun 21;2023:9856568. doi: 10.1155/2023/9856568. PMID: 35873621 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Impact of Long-Term Dienogest Therapy on Quality of Life in Asian Women with Endometriosis: the Prospective Non-Interventional Study ENVISIOeN.Reprod Sci. 2022 Apr;29(4):1157-1169. doi: 10.1007/s43032-021-00787-w. Epub 2022 Feb 2. Reprod Sci. 2022. PMID: 35112299 Free PMC article.
-
A Cross-Sectional Study on the Quality of Life in Women with Endometrioma.Int J Womens Health. 2022 Jan 11;14:9-14. doi: 10.2147/IJWH.S341603. eCollection 2022. Int J Womens Health. 2022. PMID: 35046731 Free PMC article.
-
Long-Term Administration of Dienogest for the Treatment of Pain and Intestinal Symptoms in Patients with Rectosigmoid Endometriosis.J Clin Med. 2020 Jan 6;9(1):154. doi: 10.3390/jcm9010154. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 31935969 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

