Reactivation of PTEN tumor suppressor for cancer treatment through inhibition of a MYC-WWP1 inhibitory pathway
- PMID: 31097636
- PMCID: PMC7081834
- DOI: 10.1126/science.aau0159
Reactivation of PTEN tumor suppressor for cancer treatment through inhibition of a MYC-WWP1 inhibitory pathway
Abstract
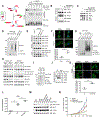
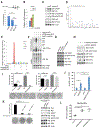
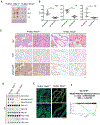
Activation of tumor suppressors for the treatment of human cancer has been a long sought, yet elusive, strategy. PTEN is a critical tumor suppressive phosphatase that is active in its dimer configuration at the plasma membrane. Polyubiquitination by the ubiquitin E3 ligase WWP1 (WW domain-containing ubiquitin E3 ligase 1) suppressed the dimerization, membrane recruitment, and function of PTEN. Either genetic ablation or pharmacological inhibition of WWP1 triggered PTEN reactivation and unleashed tumor suppressive activity. WWP1 appears to be a direct MYC (MYC proto-oncogene) target gene and was critical for MYC-driven tumorigenesis. We identified indole-3-carbinol, a compound found in cruciferous vegetables, as a natural and potent WWP1 inhibitor. Thus, our findings unravel a potential therapeutic strategy for cancer prevention and treatment through PTEN reactivation.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Comment in
-
Restoring tumor suppression.Science. 2019 May 17;364(6441):633-634. doi: 10.1126/science.aax5526. Science. 2019. PMID: 31097653 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

