Use of a CAD-CAM inferior alveolar nerve salvage template during mandibular resection for benign lesions
- PMID: 31097830
- PMCID: PMC6522861
- DOI: 10.14639/0392-100X-2408
Use of a CAD-CAM inferior alveolar nerve salvage template during mandibular resection for benign lesions
Abstract
Utilizzo di una guida CAD-CAM per la preservazione del nervo alveolare inferiore durante le resezioni mandibolari nelle lesioni benigne.
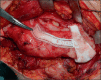
Riassunto: Durante le procedure chirurgiche di resezione mandibolare, la preservazione del nervo alveolare inferiore (NAI) è auspicabile nella patologia benigna. In questo studio pilota prospettico, riportiamo la nostra esperienza nell’uso di una dima di taglio customizzata per la rapida preservazione del nervo alveolare inferiore (RICS). La pianificazione chirurgica virtuale della guida di taglio è basata sul modello 3D ottenuto dall’elaborazione dei file DICOM della TC pre-operatoria. Sono stati inclusi nel nostro studio 5 pazienti affetti da patologia mandibolare benigna. Sono stati esteriorizzati in totale 7 NAI. Il tempo medio di esteriorizzazione è stato 23 minuti. Tutte le esteriorizzazioni sono state eseguite con successo e non è avvenuto alcun danneggiamento del fascio neuro-vascolare. Tutti i pazienti hanno mostrato il recupero completo della sensibilità del NAI entro 7 settimane dall’intervento chirurgico. In conclusione, la dima di esteriorizzazione RICS sembrerebbe permettere una più rapida e sicura preservazione del NAI.
Keywords: Computer-assisted surgery; Inferior alveolar nerve; Mandibular resection; Nerve exteriorisation.
Plain language summary
During surgical procedures involving the mandible, preserving the inferior alveolar nerve (IAN) may be preferable for benign tumours. In this prospective pilot study, we report our experience on the use of a Rapid Inferior Alveolar nerve Customised Salvage (RICS) template. Virtual surgical planning (VSP) of the template is based on a 3D model obtained from the elaboration of DICOM files of the preoperative CT scan. Five patients affected by benign mandibular pathology were included. A total of 7 IANs were exteriorised. The average time of exteriorisation was 23 minutes. All exteriorisations were performed successfully and no damage to the neuro-vascular bundle occurred. All patients showed complete recovery of sensitivity of the IAN within 7 weeks after surgical procedure. In conclusion, RICS template seems to allow faster and safer exteriorisation of the IAN.
Figures



References
-
- Mozsary PG, Syers CS. Microsurgical correction of the injured inferior alveolar nerve. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 1985;43:353-8. - PubMed
-
- Upton LG, Rajvanakarn M, Hayward JR. Evaluation of the regenerative capacity of the inferior alveolar nerve following surgical trauma. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 1987;45:212-6. - PubMed
-
- Sandstedt P, Sorensen S. Neurosensory disturbances of the trigeminal nerve: a long-term follow-up of traumatic injuries. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 1995;53:498-505. - PubMed
-
- Nocini PF, De Santis D, Fracasso E, et al. Clinical and electrophysiological assessment of inferior alveolar nerve function after lateral nerve transposition. Clin Oral Implants Res 1999;10:120-30. - PubMed
-
- Tarsitano A, Del Corso G, Ciocca L, et al. Mandibular reconstructions using computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacturing: A systematic review of a defect-based reconstructive algorithm. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 2015;43:1785-91. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

