Decreased Expression of Synaptophysin 1 (SYP1 Major Synaptic Vesicle Protein p38) and Contactin 6 (CNTN6/NB3) in the Cerebellar Vermis of reln Haplodeficient Mice
- PMID: 31098770
- PMCID: PMC11462894
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-019-00683-7
Decreased Expression of Synaptophysin 1 (SYP1 Major Synaptic Vesicle Protein p38) and Contactin 6 (CNTN6/NB3) in the Cerebellar Vermis of reln Haplodeficient Mice
Abstract
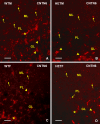
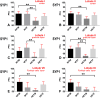
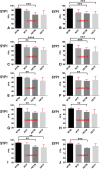
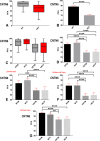
Reeler heterozygous mice (reln+/-) are seemingly normal but haplodeficient in reln, a gene implicated in autism. Structural/neurochemical alterations in the reln+/- brain are subtle and difficult to demonstrate. Therefore, the usefulness of these mice in translational research is still debated. As evidence implicated several synapse-related genes in autism and the cerebellar vermis is structurally altered in the condition, we have investigated the expression of synaptophysin 1 (SYP1) and contactin 6 (CNTN6) within the vermis of reln+/- mice. Semi-thin plastic sections of the vermis from adult mice of both sexes and different genotypes (reln+/- and reln+/+) were processed with an indirect immunofluorescence protocol. Immunofluorescence was quantified on binary images and statistically analyzed. Reln+/- males displayed a statistically significant reduction of 11.89% in the expression of SYP1 compared to sex-matched wild-type animals, whereas no differences were observed between reln+/+ and reln+/- females. In reln+/- male mice, reductions were particularly evident in the molecular layer: 10.23% less SYP1 than reln+/+ males and 5.84% < reln+/+ females. In reln+/- females, decrease was 9.84% versus reln+/+ males and 5.43% versus reln+/+ females. Both reln+/- males and females showed a stronger decrease in CNTN6 expression throughout all the three cortical layers of the vermis: 17-23% in the granular layer, 24-26% in the Purkinje cell layer, and 9-14% in the molecular layer. Altogether, decrease of vermian SYP1 and CNTN6 in reln+/- mice displayed patterns compatible with the structural modifications of the autistic cerebellum. Therefore, these mice may be a good model in translational studies.
Keywords: Cerebellum; Contactin 6; Heterozygous; Reelin; Synapses; Synaptophysin 1; Vermis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The number of Purkinje neurons and their topology in the cerebellar vermis of normal and reln haplodeficient mouse.Ann Anat. 2016 Sep;207:68-75. doi: 10.1016/j.aanat.2016.02.009. Epub 2016 Mar 17. Ann Anat. 2016. PMID: 26996540
-
Prenatal and early life diesel exhaust exposure disrupts cortical lamina organization: Evidence for a reelin-related pathogenic pathway induced by interleukin-6.Brain Behav Immun. 2019 May;78:105-115. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2019.01.013. Epub 2019 Jan 19. Brain Behav Immun. 2019. PMID: 30668980 Free PMC article.
-
Co-cultures of cerebellar slices from mice with different reelin genetic backgrounds as a model to study cortical lamination.F1000Res. 2023 Oct 2;11:1183. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.126787.2. eCollection 2022. F1000Res. 2023. PMID: 37881513 Free PMC article.
-
Reelin: Neurodevelopmental Architect and Homeostatic Regulator of Excitatory Synapses.J Biol Chem. 2017 Jan 27;292(4):1330-1338. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R116.766782. Epub 2016 Dec 19. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 27994051 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The involvement of Reelin in neurodevelopmental disorders.Neuropharmacology. 2013 May;68:122-35. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2012.08.015. Epub 2012 Sep 7. Neuropharmacology. 2013. PMID: 22981949 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Reeler Mouse: A Translational Model of Human Neurological Conditions, or Simply a Good Tool for Better Understanding Neurodevelopment?J Clin Med. 2019 Dec 1;8(12):2088. doi: 10.3390/jcm8122088. J Clin Med. 2019. PMID: 31805691 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy of Baishao Luoshi decoction on synaptic plasticity in rats with post stroke spasticity.J Tradit Chin Med. 2023 Apr;43(2):295-302. doi: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20221108.002. J Tradit Chin Med. 2023. PMID: 36994517 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ago Y, Condro MC, Tan YV, Ghiani CA, Colwell CS, Cushman JD, Fanselow MS, Hashimoto H, Waschek JA (2015) Reductions in synaptic proteins and selective alteration of prepulse inhibition in male C57BL/6 mice after postnatal administration of a VIP receptor (VIPR2) agonist. Psychopharmacology 232(12):2181–2189 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Andersen TE, Finsen B, Goffinet AM, Issinger OG, Boldyreff B (2002) A reeler mutant mouse with a new, spontaneous mutation in the reelin gene. Mol Brain Res 105(1–2):153–156 - PubMed
-
- Azevedo Frederico AC, Carvalho Ludmila RB, Grinberg LT, Farfel JM, Ferretti Renata EL, Leite Renata EP et al (2009) Equal numbers of neuronal and nonneuronal cells make the human brain an isometrically scaled-up primate brain. J Comp Neurol 513(5):532–541 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

