IL-1 receptor antagonist, anakinra, prevents myocardial dysfunction in a mouse model of Kawasaki disease vasculitis and myocarditis
- PMID: 31099056
- PMCID: PMC6718290
- DOI: 10.1111/cei.13314
IL-1 receptor antagonist, anakinra, prevents myocardial dysfunction in a mouse model of Kawasaki disease vasculitis and myocarditis
Abstract
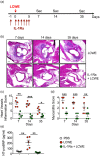
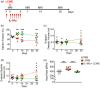
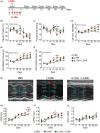
Kawasaki disease (KD) vasculitis is an acute febrile illness of childhood characterized by systemic vasculitis of unknown origin, and is the most common cause of acquired heart disease among children in the United States. While histological evidence of myocarditis can be found in all patients with acute KD, only a minority of patients are clinically symptomatic and a subset demonstrate echocardiographic evidence of impaired myocardial function, as well as increased left ventricular mass, presumed to be due to myocardial edema and inflammation. Up to a third of KD patients fail to respond to first-line therapy with intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), and the use of interleukin (IL)-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra, anakinra) is currently being investigated as an alternative therapeutic approach to treat IVIG-resistant patients. In this study, we sought to investigate the effect of IL-1Ra on myocardial dysfunction and its relation to myocarditis development during KD vasculitis. We used the Lactobacillus casei cell-wall extract (LCWE)-induced murine model of KD vasculitis and investigated the effect of IL-1Ra pretreatment on myocardial dysfunction during KD vasculitis by performing histological, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and echocardiographic evaluations. IL-1Ra pretreatment significantly reduced KD-induced myocardial inflammation and N-terminal pro B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) release. Both MRI and echocardiographic studies on LCWE-injected KD mice demonstrated that IL-1Ra pretreatment results in an improved ejection fraction and a normalized left ventricular function. These findings further support the potential beneficial effects of IL-1Ra therapy in preventing the cardiovascular complications in acute KD patients, including the myocarditis and myocardial dysfunction associated with acute KD.
Keywords: IL-1; IL-1Ra; Kawasaki disease; MRI; NT-proBNP; anakinra; echocardiogram; myocardial edema; myocarditis; vasculitis.
© 2019 The Authors. Clinical & Experimental Immunology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of British Society for Immunology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of IL-1 Ameliorates Cardiac Dysfunction and Arrhythmias in a Murine Model of Kawasaki Disease.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2024 Apr;44(4):e117-e130. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.123.320382. Epub 2024 Feb 22. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2024. PMID: 38385289 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of IL-6 in the LCWE Mouse Model of Kawasaki Disease Inhibits Acute Phase Reactant Serum Amyloid A but Fails to Attenuate Vasculitis.Front Immunol. 2021 Apr 9;12:630196. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.630196. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33897686 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term cardiovascular inflammation and fibrosis in a murine model of vasculitis induced by Lactobacillus casei cell wall extract.Front Immunol. 2024 Jun 25;15:1411979. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1411979. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38989288 Free PMC article.
-
A Comprehensive Update on Kawasaki Disease Vasculitis and Myocarditis.Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2020 Feb 5;22(2):6. doi: 10.1007/s11926-020-0882-1. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32020498
-
Myocarditis and Kawasaki disease.Int J Rheum Dis. 2018 Jan;21(1):45-49. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.13219. Epub 2017 Nov 3. Int J Rheum Dis. 2018. PMID: 29105303 Review.
Cited by
-
Myocardial perfusion impairment in children with Kawasaki disease: assessment with cardiac magnetic resonance first-pass perfusion.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024 Jul 1;14(7):4923-4935. doi: 10.21037/qims-23-1802. Epub 2024 Jun 27. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024. PMID: 39022248 Free PMC article.
-
IL-1-dependent electrophysiological changes and cardiac neural remodeling in a mouse model of Kawasaki disease vasculitis.Clin Exp Immunol. 2020 Mar;199(3):303-313. doi: 10.1111/cei.13401. Epub 2019 Dec 9. Clin Exp Immunol. 2020. PMID: 31758701 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines in the Pathogenesis of Cardiovascular Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 16;25(2):1082. doi: 10.3390/ijms25021082. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38256155 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fast recovery of cardiac function in PIMS-TS patients early using intravenous anti-IL-1 treatment.Crit Care. 2021 Apr 7;25(1):131. doi: 10.1186/s13054-021-03548-y. Crit Care. 2021. PMID: 33827651 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Beneficial effects of anti-apolipoprotein A-2 on an animal model for coronary arteritis in Kawasaki disease.Pediatr Rheumatol Online J. 2022 Dec 22;20(1):119. doi: 10.1186/s12969-022-00783-7. Pediatr Rheumatol Online J. 2022. PMID: 36550471 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McCrindle BW, Rowley AH, Newburger JW et al Diagnosis, treatment, and long‐term management of Kawasaki disease: a scientific statement for health professionals from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2017; 135:e927–e999. - PubMed
-
- Newburger JW, Takahashi M, Burns JC et al The treatment of Kawasaki syndrome with intravenous gamma globulin. N Engl J Med 1986; 315:341–7. - PubMed
-
- Burns JC, Capparelli EV, Brown JA, Newburger JW, Glode MP. Intravenous gamma‐globulin treatment and retreatment in Kawasaki disease. US/Canadian Kawasaki Syndrome Study. Group. Pediatr Infect Dis J 1998; 17:1144–8. - PubMed
-
- Sundel RP, Burns JC, Baker A, Beiser AS, Newburger JW. Gamma globulin re‐treatment in Kawasaki disease. J Pediatr 1993; 123:657–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

