Lower 5-year cup re-revision rate for dual mobility cups compared with unipolar cups: report of 15,922 cup revision cases in the Dutch Arthroplasty Register (2007-2016)
- PMID: 31099290
- PMCID: PMC6718173
- DOI: 10.1080/17453674.2019.1617560
Lower 5-year cup re-revision rate for dual mobility cups compared with unipolar cups: report of 15,922 cup revision cases in the Dutch Arthroplasty Register (2007-2016)
Abstract
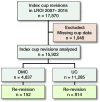
Background and purpose - During revision hip arthroplasty the dual mobility cup (DMC) is widely used to prevent dislocation despite limited knowledge of implant longevity. We determined the 5-year cup re-revision rates of DMC compared with unipolar cups (UC) following cup revisions in the Netherlands. Patients and methods - 17,870 cup revisions (index cup revision) were registered in the Dutch Arthroplasty Register during 2007-2016. Due to missing data 1,948 revisions were excluded and the remaining 15,922 were divided into 2 groups: DMC (n = 4,637) and UC (n = 11,285). Crude competing risk and multivariable Cox regression analysis were performed with cup re-revision for any reason as endpoint. Adjustments were made for known patient characteristics. Results - The use of DMC (in index cup revisions) increased from 23% (373/1,606) in 2010 to 47% (791/1,685) in 2016. Patients in the index DMC cup revision group generally had a higher ASA score and the cups were mainly cemented (89%). The main indication for index cup revision was loosening. In the DMC group dislocation was the 2nd main indication for revision. Overall 5-year cup re-revision rate was 3.5% (95% CI 3.0-4.2) for DMC and 6.7% (CI 6.3-7.2) for UC. Cup re-revision for dislocation was more frequent in the UC group compared with the DMC group (32% [261/814] versus 18% [28/152]). Stratified analyses for cup fixation showed a higher cup re-revision rate for UC in both the cemented and uncemented group. Multivariable regression analyses showed a lower risk for cup re-revision for DMC compared with UC (HR 0.5 [CI 0.4-0.6]). Interpretation - The use of DMC in cup revisions increased over time with differences in patient characteristics. The 5-year cup re-revision rates for DMC were statistically significantly lower than for UC.
Figures


References
-
- Australian Orthopaedic Association National Joint Replacement Registry Annual Report. Adelaide: AOA; 2016. https://aoanjrr.sahmri.com/documents/10180/576950/Hip%2C%20Knee%20%26%20...
-
- Australian Orthopaedic Association National Joint Replacement Registry Annual Report. Adelaide: AOA; 2017. https://aoanjrr.sahmri.com/documents/10180/397736/Hip%2C%20Knee%20%26%20...
-
- Darrith B, Courtney P M, Della Valle C J. Outcomes of dual mobility components in total hip arthroplasty: a systematic review of the literature. Bone Joint J 2018; 100-B (1): 11–19. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
