KLK3/PSA and cathepsin D activate VEGF-C and VEGF-D
- PMID: 31099754
- PMCID: PMC6588350
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.44478
KLK3/PSA and cathepsin D activate VEGF-C and VEGF-D
Abstract
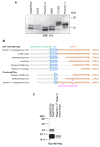
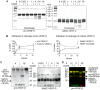
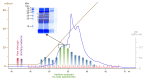
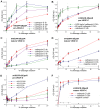
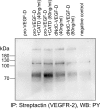
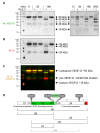
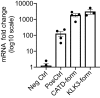
Vascular endothelial growth factor-C (VEGF-C) acts primarily on endothelial cells, but also on non-vascular targets, for example in the CNS and immune system. Here we describe a novel, unique VEGF-C form in the human reproductive system produced via cleavage by kallikrein-related peptidase 3 (KLK3), aka prostate-specific antigen (PSA). KLK3 activated VEGF-C specifically and efficiently through cleavage at a novel N-terminal site. We detected VEGF-C in seminal plasma, and sperm liquefaction occurred concurrently with VEGF-C activation, which was enhanced by collagen and calcium binding EGF domains 1 (CCBE1). After plasmin and ADAMTS3, KLK3 is the third protease shown to activate VEGF-C. Since differently activated VEGF-Cs are characterized by successively shorter N-terminal helices, we created an even shorter hypothetical form, which showed preferential binding to VEGFR-3. Using mass spectrometric analysis of the isolated VEGF-C-cleaving activity from human saliva, we identified cathepsin D as a protease that can activate VEGF-C as well as VEGF-D.
Keywords: Cathepsin D; KLK3/PSA; VEGF-C; VEGF-D; cancer biology; kallikrein-related peptidases; lymphangiogenesis; mouse.
© 2019, Jha et al.
Conflict of interest statement
SJ, KR, EC, KM, EM, HK, US, KA, MJ No competing interests declared
Figures
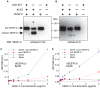
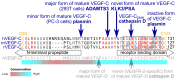

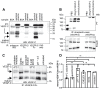

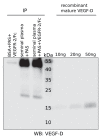
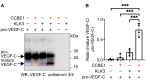

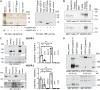

References
-
- Achen MG, Roufail S, Domagala T, Catimel B, Nice EC, Geleick DM, Murphy R, Scott AM, Caesar C, Makinen T, Alitalo K, Stacker SA. Monoclonal antibodies to vascular endothelial growth factor-D block its interactions with both VEGF receptor-2 and VEGF receptor-3. European Journal of Biochemistry. 2000;267:2505–2515. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1327.2000.01257.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Anisimov A, Alitalo A, Korpisalo P, Soronen J, Kaijalainen S, Leppänen VM, Jeltsch M, Ylä-Herttuala S, Alitalo K. Activated forms of VEGF-C and VEGF-D provide improved vascular function in skeletal muscle. Circulation Research. 2009;104:1302–1312. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.109.197830. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 265982/Academy of Finland/International
- Integrated Life Science Doctoral Program/University of Helsinki/International
- Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation programme 743155/ERC_/European Research Council/International
- Centre of Excellence Program 2014-2019, 307366/Academy of Finland/International
- 272683/Academy of Finland/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

