Assessing the occurrence and transfer dynamics of ESBL/pAmpC-producing Escherichia coli across the broiler production pyramid
- PMID: 31100096
- PMCID: PMC6524947
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0217174
Assessing the occurrence and transfer dynamics of ESBL/pAmpC-producing Escherichia coli across the broiler production pyramid
Abstract
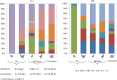
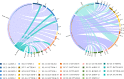
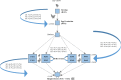
Extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL)- and plasmid mediated AmpC-type cephalosporinase (pAmpC)-producing Escherichia coli (ESBL/pAmpC E. coli) in food-producing animals is a major public health concern. This study aimed at quantifying ESBL/pAmpC-E. coli occurrence and transfer in Italy's broiler production pyramid. Three production chains of an integrated broiler company were investigated. Cloacal swabs were taken from parent stock chickens and offspring broiler flocks in four fattening farms per chain. Carcasses from sampled broiler flocks were collected at slaughterhouse. Samples were processed on selective media, and E. coli colonies were screened for ESBL/pAmpC production. ESBL/pAmpC genes and E. coli phylogroups were determined by PCR and sequencing. Average pairwise overlap of ESBL/pAmpC E. coli gene and phylogroup occurrences between subsequent production stages was estimated using the proportional similarity index, modelling uncertainty in a Monte Carlo simulation setting. In total, 820 samples were processed, from which 513 ESBL/pAmpC E. coli isolates were obtained. We found a high prevalence (92.5%, 95%CI 72.1-98.3%) in day-old parent stock chicks, in which blaCMY-2 predominated; prevalence then dropped to 20% (12.9-29.6%) at laying phase. In fattening broilers, prevalence was 69.2% (53.6-81.3%) at the start of production, 54.2% (38.9-68.6%) at slaughter time, and 61.3% (48.1-72.9%) in carcasses. Significantly decreasing and increasing trends for respectively blaCMY-2 and blaCTX-M-1 gene occurrences were found across subsequent production stages. ESBL/pAmpC E. coli genetic background appeared complex and bla-gene/phylogroup associations indicated clonal and horizontal transmission. Modelling revealed that the average transfer of ESBL/pAmpC E. coli genes between subsequent production stages was 47.7% (42.3-53.4%). We concluded that ESBL/pAmpC E. coli in the broiler production pyramid is prevalent, with substantial transfer between subsequent production levels.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- OIE. List of antimicrobial agents of veterinary importance. Paris: World Organisation for Animal Health; 2015.
-
- WHO. Critically important antimicrobials for human medicine– 5th rev. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2017.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

