Reevaluation of Historical Exposures to Ethylene Oxide Among U.S. Sterilization Workers in the National Institute of Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) Study Cohort
- PMID: 31100939
- PMCID: PMC6572526
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph16101738
Reevaluation of Historical Exposures to Ethylene Oxide Among U.S. Sterilization Workers in the National Institute of Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) Study Cohort
Abstract
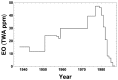
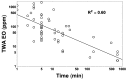
The 2016 U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Integrated Risk Information System (IRIS) assessment for ethylene oxide (EO) estimated a 10-6 increased inhalation cancer risk of 0.1 parts per trillion, based on National Institute of Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) epidemiology studies of sterilization facility workers exposed to EO between 1938 and 1986. The worker exposure estimates were based on a NIOSH statistical regression (NSR) model "validated" with EO levels measured after 1978. Between 1938 and 1978, when EO data was unavailable, the NSR model predicts exposures lowest in 1938 increasing to peak levels in 1978. That increasing EO concentration trend arose, in part, because engineering/industrial-hygiene (E/IH) factors associated with evolving EO-sterilization equipment and operations before 1978 were not properly considered in the NSR model. To test the NSR model trend prediction, a new E/IH-based model was developed using historical data on EO kill concentrations, EO residue levels in sterilized materials, post-wash EO concentrations in a sterilization chamber, and information on facility characteristics and sterilizer operator practices from operators familiar with pre-1978 industry conditions. The E/IH 90th percentile of 8 h time-weighted average EO exposures (C90) for highly exposed sterilizer operators was calibrated to match 1978 C90 values from the NSR model. E/IH model C90 exposures were estimated to decrease over time from levels 16 and were four-fold greater than NSR-estimated exposures for workers during 1938-1954 and 1955-1964. This E/IH modeled trend is opposite to that of NSR model predictions of exposures before 1978, suggesting that EPA's exclusive reliance on the NIOSH cohort to estimate EO cancer risk should be re-examined.
Keywords: cancer risk; ethylene oxide; historical occupational exposure; industrial hygiene; sterilization facilities.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. Three authors (KB, AL, PS) did this work as employees of Exponent, Inc., an engineering and health sciences consulting firm serving clients in government and industry. Decisions concerning organization, technical approach, content, preparation, editing, and submission of this manuscript were made solely by the authors and supporting technical and editorial staff at Exponent. The sponsors did not review the manuscript at any stage of development leading up to submission to the journal. The opinions of the authors do not necessarily reflect the opinions of the sponsors.
Figures



References
-
- USEPA . Evaluation of the Inhalation Carcinogenicity of Ethylene Oxide (CASRN 75-21-8) in Support of Summary Information on the Integrated Risk Information System. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Research and Development; Washington, DC, USA: 2016. EPA/635/R-16/350Fa.
-
- Stayner L., Steenland K., Greife A., Hornung R., Hayes R.B., Nowlin S., Morawetz J., Ringenburg V., Elliot L., Halperin W. Exposure-response analysis of cancer mortality in a cohort of workers exposed to ethylene oxide. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1993;138:787–798. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a116782. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

