Overall survival of patients with recurrent pancreatic cancer treated with systemic therapy: a retrospective study
- PMID: 31101022
- PMCID: PMC6525379
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-019-5630-4
Overall survival of patients with recurrent pancreatic cancer treated with systemic therapy: a retrospective study
Abstract
Background: Only a few patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) recurring after curative resection and peri-operative (neoadjuvant and adjuvant) therapy are included in clinical trials of metastatic PDAC. As such, there is a paucity of data to guide treatment after relapse, and patients are treated similarly to those with de novo metastatic PDAC (mPDAC). We evaluated the patterns of chemotherapy use and over-all survival (OS) in patients with recurrent PDAC (rPDAC) following curative therapy.
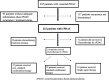
Methods: In this retrospective study, the Indiana University pancreatic cancer database was used to identify patients with PDAC who underwent curative resection and subsequently developed recurrence. Demographics, tumor and treatment characteristics were collected. Patients were broadly divided into those who received chemotherapy for rPDAC and those who did not. Patients in the former category were further subdivided into those who received single agent therapy, any standard combination therapy (5-fluorouracil/irinotecan/oxaliplatin combination or gemcitabine/nab-paclitaxel) and those who received non-standard combinations. Survival analysis was performed by the Kaplan-Meier method. Log rank tests were used to determine differences in survival between treated rPDAC patients and those not treated. Cox regression analysis was employed to evaluate factors associated with OS.
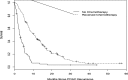
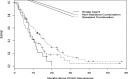
Results: We identified 435 patients with resected PDAC treated between 2008 and 2014. Two hundred and twenty-three patients (51.2%) were diagnosed with rPDAC. Of these, 140 patients (63%) received chemotherapy whereas 71 patients (32%) did not receive chemotherapy. The 74 patients (53%) who received any standard, approved multiagent combination regimen had a median OS of 14 months compared to 8 months for the 47 patents (34%) who received other non-standard combinations and the 19 (13%) who received single agent therapy (P = 0.029). Multivariate cox regression analysis showed that margin negative resection, peri-operative therapy, radiotherapy and the use of any chemotherapy for rPDAC were associated with improved OS.
Conclusion: Our findings support the use of standard approved multi-agent therapy in rPDAC. Patients derive significant benefit from these standard combination therapies with median OS that is comparable to what is observed with treatment for de novo mPDAC.
Keywords: Combination chemotherapy; FOLFIRINOX; Gemcitabine-nab paclitaxel; Metastatic pancreatic cancer; Recurrent pancreatic cancer; Recurrent pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors do not have any competing financial and non-financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Oettle H, Neuhaus P, Hochhaus A, Hartmann JT, Gellert K, Ridwelski K, Niedergethmann M, Zulke C, Fahlke J, Arning MB, et al. Adjuvant chemotherapy with gemcitabine and long-term outcomes among patients with resected pancreatic cancer: the CONKO-001 randomized trial. JAMA. 2013;310(14):1473–1481. doi: 10.1001/jama.2013.279201. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

