Educational and health outcomes of children and adolescents receiving antiepileptic medication: Scotland-wide record linkage study of 766 244 schoolchildren
- PMID: 31101093
- PMCID: PMC6525436
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-019-6888-9
Educational and health outcomes of children and adolescents receiving antiepileptic medication: Scotland-wide record linkage study of 766 244 schoolchildren
Abstract
Background: Childhood epilepsy can adversely affect education and employment in addition to health. Previous studies are small or highly selective producing conflicting results. This retrospective cohort study aims to compare educational and health outcomes of children receiving antiepileptic medication versus peers.
Methods: Record linkage of Scotland-wide databases covering dispensed prescriptions, acute and psychiatric hospitalisations, maternity records, deaths, annual pupil census, school absences/exclusions, special educational needs, school examinations, and (un)employment provided data on 766,244 children attending Scottish schools between 2009 and 2013. Outcomes were adjusted for sociodemographic and maternity confounders and comorbid conditions.
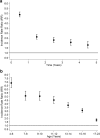
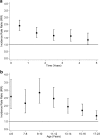
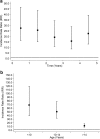
Results: Compared with peers, children on antiepileptic medication were more likely to experience school absence (Incidence Rate Ratio [IRR] 1.43, 95% CI: 1.38, 1.48), special educational needs (Odds ratio [OR] 9.60, 95% CI: 9.02, 10.23), achieve the lowest level of attainment (OR 3.43, 95% CI: 2.74, 4.29) be unemployed (OR 1.82, 95% CI: 1.60, 2.07), be admitted to hospital (Hazard Ratio [HR] 3.56, 95% CI: 3.42, 3.70), and die (HR 22.02, 95% CI: 17.00, 28.53). Absenteeism partly explained poorer attainment and higher unemployment. Girls and younger children on antiepileptic medication had higher risk of poor outcomes.
Conclusions: Children on antiepileptic medication fare worse than peers across educational and health outcomes. In order to reduce school absenteeism and mitigate its effects, children with epilepsy should receive integrated care from a multidisciplinary team that spans education and healthcare.
Keywords: Educational outcomes; Epilepsy; Health; Population cohort; Prescribing; Record linkage.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Fisher RS, Acevedo C, Arzimanoglou A, et al. ILAE official report: a practical clinical definition of epilepsy. Epilepsia. 2014;55(4):475–482. - PubMed
-
- Joint Epilepsy Council. Epilepsy prevalence, incidence and other statistics. 2011. https://d3imrogdy81qei.cloudfront.net/instructor_docs/373/29_05_2016_Joi.... Accessed 03 May 2019.
-
- Berg AT, Jallon P, Preux PM. The epidemiology of seizure disorders in infancy and childhood: definitions and classifications. Handb clinical neurol. 2013;111:391–398. - PubMed
-
- Forsgren L, Beghi E, Oun A, Sillanpaa M. The epidemiology of epilepsy in Europe – a systematic review. Eur J Neurol. 2005;12:245–253. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

