Concepts and tools for mechanism and selectivity analysis in synthetic organic electrochemistry
- PMID: 31101717
- PMCID: PMC6561265
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1904439116
Concepts and tools for mechanism and selectivity analysis in synthetic organic electrochemistry
Abstract
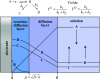
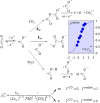
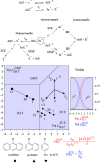
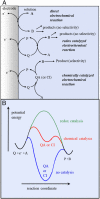
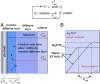
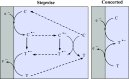
As an accompaniment to the current renaissance of synthetic organic electrochemistry, the heterogeneous and space-dependent nature of electrochemical reactions is analyzed in detail. The reactions that follow the initial electron transfer step and yield the products are intimately coupled with reactant transport. Depiction of the ensuing reactions profiles is the key to the mechanism and selectivity parameters. Analysis is eased by the steady state resulting from coupling of diffusion with convection forced by solution stirring or circulation. Homogeneous molecular catalysis of organic electrochemical reactions of the redox or chemical type may be treated in the same manner. The same benchmarking procedures recently developed for the activation of small molecules in the context of modern energy challenges lead to the establishment and comparison of the catalytic Tafel plots. At the very opposite, redox-neutral chemical reactions may be catalyzed by injection (or removal) of an electron from the electrode. This class of reactions has currently few, but very thoroughly analyzed, examples. It is likely that new cases will emerge in the near future.
Keywords: mechanism; molecular catalysis; organic electrochemistry; synthetic electrochemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Little RD, Moeller KD (2018) Introduction: Electrochemistry: Technology, synthesis, energy, and materials. Chem Rev 118:4483–4484. - PubMed
-
- Moeller KD. (2018) Using physical organic chemistry to shape the course of electrochemical reactions. Chem Rev 118:4817–4833. - PubMed
-
- Jiang Y, Xu K, Zeng C (2018) Use of electrochemistry in the synthesis of heterocyclic structures. Chem Rev 118:4485–4540. - PubMed
-
- Sauer GS, Lin S (2018) An electrocatalytic approach to the radical difunctionalization of alkenes. ACS Catal 8:5175–5187.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

