Serum metabolic signatures of coronary and carotid atherosclerosis and subsequent cardiovascular disease
- PMID: 31102408
- PMCID: PMC7963131
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz235
Serum metabolic signatures of coronary and carotid atherosclerosis and subsequent cardiovascular disease
Abstract
Aims: To characterize serum metabolic signatures associated with atherosclerosis in the coronary or carotid arteries and subsequently their association with incident cardiovascular disease (CVD).
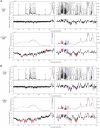
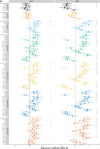
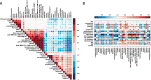
Methods and results: We used untargeted one-dimensional (1D) serum metabolic profiling by proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H NMR) among 3867 participants from the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA), with replication among 3569 participants from the Rotterdam and LOLIPOP studies. Atherosclerosis was assessed by coronary artery calcium (CAC) and carotid intima-media thickness (IMT). We used multivariable linear regression to evaluate associations between NMR features and atherosclerosis accounting for multiplicity of comparisons. We then examined associations between metabolites associated with atherosclerosis and incident CVD available in MESA and Rotterdam and explored molecular networks through bioinformatics analyses. Overall, 30 1H NMR measured metabolites were associated with CAC and/or IMT, P = 1.3 × 10-14 to 1.0 × 10-6 (discovery) and P = 5.6 × 10-10 to 1.1 × 10-2 (replication). These associations were substantially attenuated after adjustment for conventional cardiovascular risk factors. Metabolites associated with atherosclerosis revealed disturbances in lipid and carbohydrate metabolism, branched chain, and aromatic amino acid metabolism, as well as oxidative stress and inflammatory pathways. Analyses of incident CVD events showed inverse associations with creatine, creatinine, and phenylalanine, and direct associations with mannose, acetaminophen-glucuronide, and lactate as well as apolipoprotein B (P < 0.05).
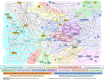
Conclusion: Metabolites associated with atherosclerosis were largely consistent between the two vascular beds (coronary and carotid arteries) and predominantly tag pathways that overlap with the known cardiovascular risk factors. We present an integrated systems network that highlights a series of inter-connected pathways underlying atherosclerosis.
Keywords: Atherosclerosis; Coronary artery calcium; Epidemiological studies; Intima-media thickness; Metabolic phenotyping; Metabolomics.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Figures





Comment in
-
Atherosclerotic metabolites: basic science is progressing, so we need to think about clinical implications.Eur Heart J. 2019 Sep 7;40(34):2897-2898. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz252. Eur Heart J. 2019. PMID: 31102399 No abstract available.
References
-
- Timmis A, Townsend N, Gale C, Grobbee R, Maniadakis N, Flather M, Wilkins E, Wright L, Vos R, Bax J, Blum M, Pinto F, Vardas P, Goda A, Demiraj AF, Weidinger F, Metzler B, Ibrahimov F, Pasquet AA, Claeys M, Thorton Y, Kusljugic Z, Smajic E, Velchev V, Ivanov N, Antoniades L, Agathangelou P, Táborský M, Gerdes C, Viigima M, Juhani PM, Juilliere Y, Cattan S, Aladashvili A, Hamm C, Kuck K-H, Papoutsis K, Bestehorn K, Foussas S, Giannoulidou G, Varounis C, Kallikazaros I, Kiss RG, Czétényi T, Becker D, Gudnason T, Kearney P, McDonald K, Rozenman Y, Ziv B, Bolognese L, Luciolli P, Boriani G, Berkinbayev S, Rakisheva A, Mirrakhimov E, Erglis A, Jegere S, Marinskis G, Beissel J, Marchal N, Kedev S, Xuereb RG, Tilney T, Felice T, Popovici M, Bax J, Mulder B, Simoons M, Elsendoorn M, Steigen TK, Atar D, Kalarus Z, Tendera M, Cardoso JS, Ribeiro J, Mateus C, Tatu-Chitoiu G, Seferovic P, Beleslin B, Simkova I, Durcikova P, Belicova V, Fras Z, Radelj S, Gonzalez Juanatey JR, Legendre S, Braunschweig F, Kaufmann UP, Rudiger-Sturchler M, Tokgozoglu L, Unver A, Kovalenko V, Nesukay E, Naum A, de Courtelary PT, Martin S, Sebastiao D, Ghislain D, Bardinet I, Logstrup S.. European Society of Cardiology: cardiovascular disease statistics 2017. Eur Heart J 2018;39:508–579. - PubMed
-
- Tzoulaki I, Elliott P, Kontis V, Ezzati M.. Worldwide exposures to cardiovascular risk factors and associated health effects: current knowledge and data gaps. Circulation 2016;133:2314–2333. - PubMed
-
- Herrington DM, Mao C, Parker SJ, Fu Z, Yu G, Chen L, Venkatraman V, Fu Y, Wang Y, Howard TD, Jun G, Zhao CF, Liu Y, Saylor G, Spivia WR, Athas GB, Troxclair D, Hixson JE, Vander Heide RS, Wang Y, Van Eyk JE.. Proteomic architecture of human coronary and aortic atherosclerosis. Circulation 2018;137:2741–2756. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- HHSN268201500003C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095161/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL133932/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 212945/Z/18/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MR/L01632X/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- N01 HC095167/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MR/L01341X/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- N01 HC095159/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N02 HL64278/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001420/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095163/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000040/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095166/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095162/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HPRU-2012-10141/DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- N01 HC095160/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095168/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN263201500003I/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001079/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N02 HL064278/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095169/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201500003I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL111362/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001881/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095165/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095164/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States

