CD55 Is Essential for CD103+ Dendritic Cell Tolerogenic Responses that Protect against Autoimmunity
- PMID: 31103439
- PMCID: PMC6617008
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2019.04.008
CD55 Is Essential for CD103+ Dendritic Cell Tolerogenic Responses that Protect against Autoimmunity
Abstract
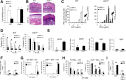
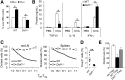
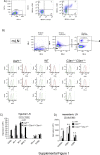
Recent studies traced inflammatory bowel disease in some patients to deficiency of CD55 [decay-accelerating factor (DAF)], but the mechanism underlying the linkage remained unclear. Herein, we studied the importance of DAF in enabling processes that program tolerance in the gut and the eye, two immune-privileged sites where immunosuppressive responses are continuously elicited. Unlike oral feeding or ocular injection of ovalbumin in wild-type (WT) mice, which induced dominant immune tolerance, identical treatment of DAF-/- mice or DAF-/- to WT bone marrow chimeras did not. While 10% to 30% of mesenteric and submandibular lymph node CD4+ cells became robust T-regulatory cells (Tregs) in WT forkhead box P3 (Foxp3)-green fluorescent protein mice, few in either site became Tregs with little suppressor activity in DAF-/- Foxp3-green fluorescent protein mice. Phenotyping of CD103+ dendritic cells (DCs) from the ovalbumin-fed DAF-/- mice showed impaired expression of inducer of costimulation (ICOS) ligand, programmed death receptor 1-ligand 1 (PD1-L1), CxxxC chemokine receptor 1 (Cx3CR1), CCR7, and CCR9. Analyses of elicited DAF-/- Foxp3+ Tregs showed reduced expression of interferon regulatory factor 8 (IRF-8)/aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 family member A2 (Aldh1a2) and glycoprotein A repetitions predominant/latency-associated protein associated with Treg transforming growth factor-β production and presentation, as well as integrin β6/integrin β8 associated with Treg and CD103+ DC transforming growth factor-β release. Thus, DAF is required for the properties of CD103+ DCs and their naïve CD4+ cell partners that together program tolerance.
Copyright © 2019 American Society for Investigative Pathology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures






References
-
- Niederkorn J., Streilein J.W., Shadduck J.A. Deviant immune responses to allogeneic tumors injected intracamerally and subcutaneously in mice. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1981;20:355–363. - PubMed
- Niederkorn J, Streilein JW, Shadduck JA: Deviant immune responses to allogeneic tumors injected intracamerally and subcutaneously in mice. Investigative ophthalmology & visual science 1981, 20:355-363. - PubMed
-
- Niederkorn J.Y., Streilein J.W. Alloantigens placed into the anterior chamber of the eye induce specific suppression of delayed-type hypersensitivity but normal cytotoxic T lymphocyte and helper T lymphocyte responses. J Immunol. 1983;131:2670–2674. - PubMed
- Niederkorn JY, Streilein JW: Alloantigens placed into the anterior chamber of the eye induce specific suppression of delayed-type hypersensitivity but normal cytotoxic T lymphocyte and helper T lymphocyte responses. Journal of immunology 1983, 131:2670-2674. - PubMed
-
- McKenna K.C., Xu Y., Kapp J.A. Injection of soluble antigen into the anterior chamber of the eye induces expansion and functional unresponsiveness of antigen-specific CD8+ T cells. J Immunol. 2002;169:5630–5637. - PubMed
- McKenna KC, Xu Y, Kapp JA: Injection of soluble antigen into the anterior chamber of the eye induces expansion and functional unresponsiveness of antigen-specific CD8+ T cells. Journal of immunology 2002, 169:5630-5637. - PubMed
-
- Streilein J.W., Niederkorn J.Y., Shadduck J.A. Systemic immune unresponsiveness induced in adult mice by anterior chamber presentation of minor histocompatibility antigens. J Exp Med. 1980;152:1121–1125. - PMC - PubMed
- Streilein JW, Niederkorn JY, Shadduck JA: Systemic immune unresponsiveness induced in adult mice by anterior chamber presentation of minor histocompatibility antigens. J Exp Med 1980, 152:1121-1125. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

