MicroRNAs are Necessary for BMP-7-induced Dendritic Growth in Cultured Rat Sympathetic Neurons
- PMID: 31104181
- PMCID: PMC6713596
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-019-00688-2
MicroRNAs are Necessary for BMP-7-induced Dendritic Growth in Cultured Rat Sympathetic Neurons
Abstract
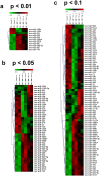
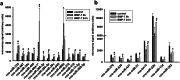
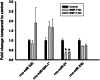
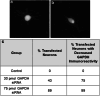
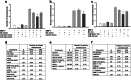
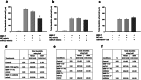
Neuronal connectivity is dependent on size and shape of the dendritic arbor. However, mechanisms controlling dendritic arborization, especially in the peripheral nervous system, are not completely understood. Previous studies have shown that bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) are important initiators of dendritic growth in peripheral neurons. In this study, we examined the hypothesis that post-transcriptional regulation mediated by microRNAs (miRNAs) is necessary for BMP-7-induced dendritic growth in these neurons. To examine the role of miRNAs in BMP-7-induced dendritic growth, microarray analyses was used to profile miRNA expression in cultured sympathetic neurons from the superior cervical ganglia of embryonic day 21 rat pups at 6 and 24 h after treatment with BMP-7 (50 ng/mL). Our data showed that BMP-7 significantly regulated the expression of 43 of the 762 miRNAs. Of the 43 miRNAs, 22 showed robust gene expression; 14 were upregulated by BMP-7 and 8 were downregulated by BMP-7. The expression profile for miR-335, miR-664-1*, miR-21, and miR-23b was confirmed using qPCR analyses. Functional studies using morphometric analyses of dendritic growth in cultured sympathetic neurons transfected with miRNA mimics and inhibitors indicated that miR-664-1*, miR-23b, and miR-21 regulated early stages of BMP-7-induced dendritic growth. In summary, our data provide evidence for miRNA-mediated post-transcriptional regulation as important downstream component of BMP-7 signaling during early stages of dendritic growth in sympathetic neurons.
Keywords: Bone morphogenetic proteins; Dendrite; MicroRNA; Sympathetic neurons.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Transcriptional responses of cultured rat sympathetic neurons during BMP-7-induced dendritic growth.PLoS One. 2011;6(7):e21754. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0021754. Epub 2011 Jul 13. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21765909 Free PMC article.
-
Bone morphogenetic protein-5 (BMP-5) promotes dendritic growth in cultured sympathetic neurons.BMC Neurosci. 2001;2:12. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-2-12. Epub 2001 Sep 11. BMC Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11580864 Free PMC article.
-
Reactive oxygen species are involved in BMP-induced dendritic growth in cultured rat sympathetic neurons.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2015 Jul;67:116-25. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2015.06.007. Epub 2015 Jun 14. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26079955 Free PMC article.
-
Glia induce dendritic growth in cultured sympathetic neurons by modulating the balance between bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) and BMP antagonists.J Neurosci. 2002 Dec 1;22(23):10377-87. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-23-10377.2002. J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 12451137 Free PMC article.
-
Bone morphogenetic proteins.Growth Factors. 2004 Dec;22(4):233-41. doi: 10.1080/08977190412331279890. Growth Factors. 2004. PMID: 15621726 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Bmp- and Fgf Signaling Modulating Mouse Proepicardium Cell Fate.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Jan 4;9:757781. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.757781. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35059396 Free PMC article.
-
The sympathetic nervous system in development and disease.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2021 Nov;22(11):685-702. doi: 10.1038/s41583-021-00523-y. Epub 2021 Oct 1. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34599308 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Crosstalk between Bone and Nerves within Bone.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021 Feb 10;8(7):2003390. doi: 10.1002/advs.202003390. eCollection 2021 Apr. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021. PMID: 33854888 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-140-3p exhibits repressive functions on preosteoblast viability and differentiation by downregulating MCF2L in osteoporosis.In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2020 Jan;56(1):49-58. doi: 10.1007/s11626-019-00405-9. Epub 2019 Nov 15. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2020. PMID: 31732956
References
-
- Bruckenstein DA, Higgins D (1988) Morphological differentiation of embryonic rat sympathetic neurons in tissue culture. Dev Biol 128:337–348. 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90296-5 - PubMed
-
- Caceres A, Banker G, Steward O et al (1984) MAP2 is localized to the dendrites of hippocampal neurons which develop in culture. Brain Res 315:314–318 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

