Genetic knockout of myosin light chain kinase (MLCK210) prevents cerebral microhemorrhages and attenuates neuroinflammation in a mouse model of vascular cognitive impairment and dementia
- PMID: 31104189
- PMCID: PMC6885026
- DOI: 10.1007/s11357-019-00072-4
Genetic knockout of myosin light chain kinase (MLCK210) prevents cerebral microhemorrhages and attenuates neuroinflammation in a mouse model of vascular cognitive impairment and dementia
Abstract
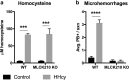
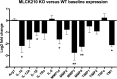
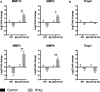
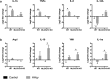
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is critical in maintenance of brain homeostasis, and loss of its functional integrity is a key feature across a broad range of neurological insults. This includes both acute injuries such as traumatic brain injury and stroke, as well as more chronic pathologies associated with aging, such as vascular cognitive impairment and dementia (VCID). A specific form of myosin light chain kinase (MLCK210) is a major regulator of barrier integrity in general, including the BBB. Studies have demonstrated the potential of MLCK210 as a therapeutic target for peripheral disorders involving tissue barrier dysfunction, but less is known about its potential as a target for chronic neurologic disorders. We report here that genetic knockout (KO) of MLCK210 protects against cerebral microhemorrhages and neuroinflammation induced by chronic dietary hyperhomocysteinemia. Overall, the results are consistent with an accumulating body of evidence supporting MLCK210 as a potential therapeutic target for tissue barrier dysfunction and specifically implicate it in BBB dysfunction and neuroinflammation in a model of VCID.
Keywords: Cerebrovascular; Knockout; Microhemorrhage; Myosin light chain kinase; Neuroinflammation; Vascular cognitive impairment and dementia.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Time-course of glial changes in the hyperhomocysteinemia model of vascular cognitive impairment and dementia (VCID).Neuroscience. 2017 Jan 26;341:42-51. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2016.11.024. Epub 2016 Nov 25. Neuroscience. 2017. PMID: 27890830 Free PMC article.
-
Time course of neuropathological events in hyperhomocysteinemic amyloid depositing mice reveals early neuroinflammatory changes that precede amyloid changes and cerebrovascular events.J Neuroinflammation. 2019 Dec 30;16(1):284. doi: 10.1186/s12974-019-1685-z. J Neuroinflammation. 2019. PMID: 31888650 Free PMC article.
-
MLCK210 gene knockout or kinase inhibition preserves lung function following endotoxin-induced lung injury in mice.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2007 Jun;292(6):L1327-34. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00380.2006. Epub 2007 Feb 16. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17307813
-
Vascular cognitive impairment: Modeling a critical neurologic disease in vitro and in vivo.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 May;1862(5):975-82. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2015.12.009. Epub 2015 Dec 17. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26704178 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Transcription Factor Nrf2 (Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-Related Factor 2) for the Intervention of Vascular Cognitive Impairment and Dementia.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2021 Jan;41(1):97-116. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.120.314804. Epub 2020 Oct 15. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2021. PMID: 33054394 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Accelerated cerebral vascular injury in diabetes is associated with vascular smooth muscle cell dysfunction.Geroscience. 2020 Apr;42(2):547-561. doi: 10.1007/s11357-020-00179-z. Epub 2020 Mar 12. Geroscience. 2020. PMID: 32166556 Free PMC article.
-
Progression of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in mice and neutrophil-mediated blood-brain barrier dysfunction requires non-muscle myosin light chain kinase.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2025 Jun;45(6):1203-1220. doi: 10.1177/0271678X251318620. Epub 2025 Feb 7. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2025. PMID: 39917847 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA SLC16A1-AS1 is Upregulated in Glioblastoma and Promotes Cancer Cell Proliferation by Regulating miR-149 Methylation.Cancer Manag Res. 2021 Feb 10;13:1215-1223. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S264613. eCollection 2021. Cancer Manag Res. 2021. PMID: 33603467 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical implication of cellular vaccine in glioma: current advances and future prospects.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Nov 23;39(1):257. doi: 10.1186/s13046-020-01778-6. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 33228738 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IGF1R deficiency in vascular smooth muscle cells impairs myogenic autoregulation and cognition in mice.Front Aging Neurosci. 2024 Feb 15;16:1320808. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2024.1320808. eCollection 2024. Front Aging Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38425784 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al-Sadi R, Youssef M, Rawat M, Guo S, Dokladny K, Haque M, Watterson DM, Ma TY. MMP9-induced increase in intestinal epithelial tight permeability is mediated by p38 kinase signaling pathway activation of MLCK gene. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2019;316:G278–G290. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00126.2018. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arnaud C, Bouyon S, Recoquillon S, Brasseur S, Lemari E, Briancon-Marjollet A, Gonthier B, Toral M, Faury G, Martinez C, Andriantsitohaina R, Pepin JL. Nonmuscle myosin light chain kinase: a key player in intermittent hypoxia-induced vascular alterations. J Am Heart Assoc. 2018;7:e007893. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.117.007893. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beard RS, Haines RJ, Wu KY, Reynolds JJ, Davis SM, Elliott JE, Malinin NL, Chatterjee V, Cha BJ, Wu MH, Yuan SY. Non-muscle MLCK is required for β-catenin-and FoxO1-dependent downregulation of Cldn5 in IL-1β-mediated barrier dysfunction in brain endothelial cells. J Cell Sci. 2014;127:1840–1853. doi: 10.1242/jcs.144550. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Benjamini Y, Krieger AM, Yekutieli D. Adaptive linear step-up procedures that control the false discovery rate. Biometrika. 2006;93:491–507. doi: 10.1093/biomet/93.3.491. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

