Biomimetic Cationic Nanoparticles Based on Silica: Optimizing Bilayer Deposition from Lipid Films
- PMID: 31105181
- PMCID: PMC6352667
- DOI: 10.3390/biomimetics2040020
Biomimetic Cationic Nanoparticles Based on Silica: Optimizing Bilayer Deposition from Lipid Films
Abstract
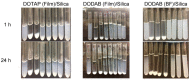
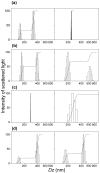
The optimization of bilayer coverage on particles is important for a variety of biomedical applications, such as drug, vaccine, and genetic material delivery. This work aims at optimizing the deposition of cationic bilayers on silica over a range of experimental conditions for the intervening medium and two different assemblies for the cationic lipid, namely, lipid films or pre-formed lipid bilayer fragments. The lipid adsorption on silica in situ over a range of added lipid concentrations was determined from elemental analysis of carbon, hydrogen, and nitrogen and related to the colloidal stability, sizing, zeta potential, and polydispersity of the silica/lipid nanoparticles. Superior bilayer deposition took place from lipid films, whereas adsorption from pre-formed bilayer fragments yielded limiting adsorption below the levels expected for bilayer adsorption.
Keywords: AEROSIL OX-50; N-[1-(2,3-dioleoyloxy)propyl]-N,N,N-trimethylammonium chloride; cationic bilayer fragments; colloidal stability; dioctadecyldimethylammonium bromide; elemental analysis for in situ adsorption; films of cationic lipids; optimal bilayer adsorption from films.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Cationic Nanostructures for Vaccines Design.Biomimetics (Basel). 2020 Jul 7;5(3):32. doi: 10.3390/biomimetics5030032. Biomimetics (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32645946 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomimetic particles: optimization of phospholipid bilayer coverage on silica and colloid stabilization.Langmuir. 2005 Oct 25;21(22):10160-4. doi: 10.1021/la0504614. Langmuir. 2005. PMID: 16229540
-
Adsorption behavior of DODAB/DPPC vesicles on silica.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2007 Sep 15;313(2):519-26. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2007.04.061. Epub 2007 May 3. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2007. PMID: 17532328
-
Cationic Biomimetic Particles of Polystyrene/Cationic Bilayer/Gramicidin for Optimal Bactericidal Activity.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2017 Dec 2;7(12):422. doi: 10.3390/nano7120422. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2017. PMID: 29207496 Free PMC article.
-
Biomimetic nanoparticles: preparation, characterization and biomedical applications.Int J Nanomedicine. 2010 Apr 7;5:249-59. doi: 10.2147/ijn.s9035. Int J Nanomedicine. 2010. PMID: 20463941 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Biosafety of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles.Biomimetics (Basel). 2018 Aug 15;3(3):22. doi: 10.3390/biomimetics3030022. Biomimetics (Basel). 2018. PMID: 31105244 Free PMC article.
-
Cationic and Biocompatible Polymer/Lipid Nanoparticles as Immunoadjuvants.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Nov 4;13(11):1859. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13111859. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34834275 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization and Differential Cytotoxicity of Gramicidin Nanoparticles Combined with Cationic Polymer or Lipid Bilayer.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Sep 27;14(10):2053. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14102053. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36297488 Free PMC article.
-
Cationic Nanostructures for Vaccines Design.Biomimetics (Basel). 2020 Jul 7;5(3):32. doi: 10.3390/biomimetics5030032. Biomimetics (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32645946 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Supramolecular Nanostructures for Vaccines.Biomimetics (Basel). 2021 Dec 29;7(1):6. doi: 10.3390/biomimetics7010006. Biomimetics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 35076466 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Carmona-Ribeiro A.M., Midmore B.R. Synthetic bilayer adsorption onto polystyrene microspheres. Langmuir. 1992;8:801–806. doi: 10.1021/la00039a013. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

