A Highly Stretchable, Tough, Fast Self-Healing Hydrogel Based on Peptide⁻Metal Ion Coordination
- PMID: 31105221
- PMCID: PMC6632049
- DOI: 10.3390/biomimetics4020036
A Highly Stretchable, Tough, Fast Self-Healing Hydrogel Based on Peptide⁻Metal Ion Coordination
Abstract
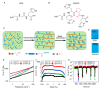
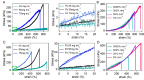
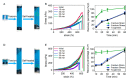
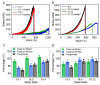
Metal coordination bonds are widely used as the dynamic cross-linkers to construct self-healing hydrogels. However, it remains challenging to independently improve the toughness of metal coordinated hydrogels without affecting the stretchability and self-healing properties, as all these features are directly correlated with the dynamic properties of the same metal coordination bonds. In this work, using histidine-Zn2+ binding as an example, we show that the coordination number (the number of binding sites in each cross-linking ligand) is an important parameter for the mechanical strength of the hydrogels. By increasing the coordination number of the binding site, the mechanical strength of the hydrogels can be greatly improved without sacrificing the stretchability and self-healing properties. By adjusting the peptide and Zn2+ concentrations, the hydrogels can achieve a set of demanding mechanical features, including the Young's modulus of 7-123 kPa, fracture strain of 434-781%, toughness of 630-1350 kJ m-3, and self-healing time of ~1 h. We anticipate the engineered hydrogels can find broad applications in a variety of biomedical fields. Moreover, the concept of improving the mechanical strength of metal coordinated hydrogels by tuning the coordination number may inspire the design of other dynamically cross-linked hydrogels with further improved mechanical performance.
Keywords: hydrogel; metal ion coordination; self-healing; stretch-ability.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Integration of Macro-Cross-Linker and Metal Coordination: A Super Stretchable Hydrogel with High Toughness.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020 Sep 9;12(36):40786-40793. doi: 10.1021/acsami.0c11167. Epub 2020 Aug 25. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020. PMID: 32805982
-
Tough, Stretchable, Compressive Novel Polymer/Graphene Oxide Nanocomposite Hydrogels with Excellent Self-Healing Performance.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017 Nov 1;9(43):38052-38061. doi: 10.1021/acsami.7b12932. Epub 2017 Oct 23. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017. PMID: 29019393
-
Tough, Healable, and Sensitive Strain Sensor Based on Multiphysically Cross-Linked Hydrogel for Ionic Skin.Biomacromolecules. 2023 Mar 13;24(3):1287-1298. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.2c01335. Epub 2023 Feb 6. Biomacromolecules. 2023. PMID: 36745900
-
Self-Healing Polymeric Hydrogel Formed by Metal-Ligand Coordination Assembly: Design, Fabrication, and Biomedical Applications.Macromol Rapid Commun. 2019 Apr;40(7):e1800837. doi: 10.1002/marc.201800837. Epub 2019 Jan 23. Macromol Rapid Commun. 2019. PMID: 30672628 Review.
-
On the Race for More Stretchable and Tough Hydrogels.Gels. 2019 Apr 28;5(2):24. doi: 10.3390/gels5020024. Gels. 2019. PMID: 31035400 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Peptide-Based Materials That Exploit Metal Coordination.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 27;24(1):456. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010456. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36613898 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioinspired structural hydrogels with highly ordered hierarchical orientations by flow-induced alignment of nanofibrils.Nat Commun. 2024 Jan 2;15(1):118. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-44481-8. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38168050 Free PMC article.
-
Halogen bonding regulated functional nanomaterials.Nanoscale Adv. 2021 Sep 23;3(22):6342-6357. doi: 10.1039/d1na00485a. eCollection 2021 Nov 9. Nanoscale Adv. 2021. PMID: 36133496 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The molecular mechanisms underlying mussel adhesion.Nanoscale Adv. 2019 Oct 10;1(11):4246-4257. doi: 10.1039/c9na00582j. eCollection 2019 Nov 5. Nanoscale Adv. 2019. PMID: 36134404 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in the Design of Phenylboronic Acid-Based Glucose-Sensitive Hydrogels.Polymers (Basel). 2023 Jan 23;15(3):582. doi: 10.3390/polym15030582. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36771883 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Li Q., Liu C., Wen J., Wu Y., Shan Y., Liao J. The design, mechanism and biomedical application of self-healing hydrogels. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2017;28:1857–1874. doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2017.05.007. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

