Biosafety of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles
- PMID: 31105244
- PMCID: PMC6352691
- DOI: 10.3390/biomimetics3030022
Biosafety of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles
Abstract
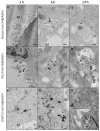
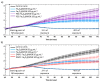
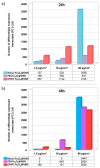
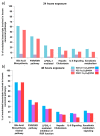
Careful analysis of any new nanomedicine device or disposal should be undertaken to comprehensively characterize the new product before application, so that any unintended side effect is minimized. Because of the increasing number of nanotechnology-based drugs, we can anticipate that regulatory authorities might adapt the approval process for nanomedicine products due to safety concerns, e.g., request a more rigorous testing of the potential toxicity of nanoparticles (NPs). Currently, the use of mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSN) as drug delivery systems is challenged by a lack of data on the toxicological profile of coated or non-coated MSN. In this context, we have carried out an extensive study documenting the influence of different functionalized MSN on the cellular internalization and in vivo behaviour. In this article, a synthesis of these works is reviewed and the perspectives are drawn. The use of magnetic MSN (Fe3O4@MSN) allows an efficient separation of coated NPs from cell cultures with a simple magnet, leading to results regarding corona formation without experimental bias. Our interest is focused on the mechanism of interaction with model membranes, the adsorption of proteins in biological fluids, the quantification of uptake, and the effect of such NPs on the transcriptomic profile of hepatic cells that are known to be readily concerned by NPs' uptake in vivo, especially in the case of an intravenous injection.
Keywords: adverse outcome pathways; internalization; mesoporous silica; nanoparticles; protein corona; safety.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Figures






References
-
- Chang B., Guo J., Liu C., Qian J., Yang W. Surface functionalization of magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles for controlled drug release. J. Mater. Chem. 2010;20:9941. doi: 10.1039/c0jm01237h. - DOI
-
- Perrier M., Gary-Bobo M., Lartigue L., Brevet D., Morère A., Garcia M., Maillard P., Raehm L., Guari Y., Larionova J., et al. Mannose-functionalized porous silica-coated magnetic nanoparticles for two-photon imaging or PDT of cancer cells. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2013;15:1602. doi: 10.1007/s11051-013-1602-9. - DOI
-
- Nyalosaso J.L., Rascol E., Pisani C., Dorandeu C., Dumail X., Maynadier M., Gary-Bobo M., Kee Him J.L., Bron P., Garcia M., et al. Synthesis, decoration, and cellular effects of magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2016;6:57275–57283. doi: 10.1039/C6RA09017F. - DOI
-
- Rascol E., Daurat M., Da Silva A., Maynadier M., Dorandeu C., Charnay C., Garcia M., Lai-Kee-Him J., Bron P., Auffan M., et al. Biological fate of Fe3O4 core-shell mesoporous silica nanoparticles depending on particle surface chemistry. Nanomaterials. 2017;7:162. doi: 10.3390/nano7070162. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pisani C., Gaillard J.-C., Odorico M., Nyalosaso J.L., Charnay C., Guari Y., Chopineau J., Devoisselle J.-M., Armengaud J., Prat O. The timeline of corona formation around silica nanocarriers highlights the role of the protein interactome. Nanoscale. 2017;9:1840–1851. doi: 10.1039/C6NR04765C. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

