Fiber Embroidery of Self-Sensing Soft Actuators
- PMID: 31105246
- PMCID: PMC6352685
- DOI: 10.3390/biomimetics3030024
Fiber Embroidery of Self-Sensing Soft Actuators
Abstract
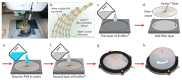
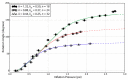
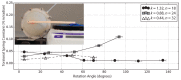
Natural organisms use a combination of contracting muscles and inextensible fibers to transform into controllable shapes, camouflage into their surrounding environment, and catch prey. Replicating these capabilities with engineered materials is challenging because of the difficulty in manufacturing and controlling soft material actuators with embedded fibers. In addition, while linear and bending motions are common in soft actuators, rotary motions require three-dimensional fiber wrapping or multiple bending or linear elements working in coordination that are challenging to design and fabricate. In this work, an automatic embroidery machine patterned Kevlar™ fibers and stretchable optical fibers into inflatable silicone membranes to control their inflated shape and enable sensing. This embroidery-based fabrication technique is simple, low cost, and allows for precise and custom patterning of fibers in elastomers. Using this technique, we developed inflatable elastomeric actuators embedded with a planar spiral pattern of high-strength Kevlar™ fibers that inflate into radially symmetric shapes and achieve nearly 180° angular rotation and 10 cm linear displacement.
Keywords: elastomer; shape-changing; soft actuators; twisting.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Additive Manufacture of Composite Soft Pneumatic Actuators.Soft Robot. 2018 Dec;5(6):726-736. doi: 10.1089/soro.2018.0030. Epub 2018 Aug 27. Soft Robot. 2018. PMID: 30148682
-
Fabrication of Soft Pneumatic Network Actuators with Oblique Chambers.J Vis Exp. 2018 Aug 17;(138):58277. doi: 10.3791/58277. J Vis Exp. 2018. PMID: 30176026 Free PMC article.
-
Dielectric Elastomer Actuator Driven Soft Robotic Structures With Bioinspired Skeletal and Muscular Reinforcement.Front Robot AI. 2020 Dec 15;7:510757. doi: 10.3389/frobt.2020.510757. eCollection 2020. Front Robot AI. 2020. PMID: 33501298 Free PMC article.
-
Additive Manufacturing of Liquid Crystal Elastomer Actuators Based on Knitting Technology.Adv Mater. 2023 Sep;35(36):e2302706. doi: 10.1002/adma.202302706. Epub 2023 Jul 20. Adv Mater. 2023. PMID: 37278691
-
Bioinspired Synergistic Fluorescence-Color-Switchable Polymeric Hydrogel Actuators.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2019 Nov 4;58(45):16243-16251. doi: 10.1002/anie.201908437. Epub 2019 Sep 24. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2019. PMID: 31475456 Review.
Cited by
-
Single-vat single-cure grayscale digital light processing 3D printing of materials with large property difference and high stretchability.Nat Commun. 2023 Mar 6;14(1):1251. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-36909-y. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 36878943 Free PMC article.
-
Design and Computational Modeling of Fabric Soft Pneumatic Actuators for Wearable Assistive Devices.Sci Rep. 2020 Jun 15;10(1):9638. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-65003-2. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32541650 Free PMC article.
-
Neural Network-Based Active Load-Sensing Scheme and Stiffness Adjustment for Pneumatic Soft Actuators for Minimally Invasive Surgery Support.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Jan 11;23(2):833. doi: 10.3390/s23020833. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36679629 Free PMC article.
-
Soft Robotics.Biomimetics (Basel). 2019 Mar 12;4(1):22. doi: 10.3390/biomimetics4010022. Biomimetics (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31105207 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Van Leeuwen J.L., De Groot J.H., Kier W.M. Evolutionary mechanics of protrusible tentacles and tongues. Neth. J. Zool. 2000;50:113–119. doi: 10.1163/156854200X00036. - DOI
-
- Van Leeuwen J.L., Kier W.M. Functional design of tentacles in squid: Linking sarcomere ultrastructure to gross morphological dynamics. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1997;352:551–571. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1997.0038. - DOI
-
- Kier W., Leeuwen J. A kinematic analysis of tentacle extension in the squid Loligo pealei. J. Exp. Biol. 1997;200:41–53. - PubMed
-
- Yao L., Niiyama R., Ou J., Follmer S., Della Silva C., Ishii H. PneUI: Pneumatically Actuated Soft Composite Materials for Shape Changing Interfaces; Proceedings of the 26th annual ACM symposium on User interface software and technology; St. Andrews, UK. 8–11 October 2013; pp. 13–22.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

