Design, Additive Manufacture, and Control of a Pneumatic, MR-Compatible Needle Driver
- PMID: 31105476
- PMCID: PMC6519471
- DOI: 10.1109/TRO.2015.2504981
Design, Additive Manufacture, and Control of a Pneumatic, MR-Compatible Needle Driver
Abstract
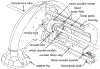
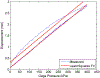
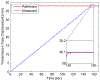
This paper reports the design, modeling, and control of an MR-compatible actuation unit comprising pneumatic stepper mechanisms. One helix-shaped bellows and one toroid-shaped bellows were designed to actuate in pure rotation and pure translation, respectively. The actuation unit is a two degree- of-freedom needle driver that translates and rotates the base of one tube of a steerable needle like a concentric tube robot. For safety, mechanical stops limit needle motion to maximum unplanned step sizes of 0.5 mm and 0.5 degrees. Additively manufactured by selective laser sintering, the flexible fluidic actuating (FFA) mechanism achieves two degree-of-freedom motion as a monolithic, compact, and hermetically-sealed device. A second novel contribution is sub-step control for precise translations and rotations less than full step increments; steady- state errors of 0.013 mm and 0.018 degrees were achieved. The linear FFA produced peak forces of 33 N and -26.5 N for needle insertion and retraction, respectively. The rotary FFA produced bidirectional peak torques of 68 N-mm. With the FFA's in full motion in a 3T scanner, no loss in signal-to-noise ratio of MR images observed.
Keywords: Magnetic resonance compatible; additively manufactured actuator; concentric tube robot; flexible fluidic actuator; medical robotics; pneumatic systems; sliding mode control; stepper motor.
Figures







Similar articles
-
An MR-conditional high-torque pneumatic stepper motor for MRI-guided and robot-assisted intervention.Ann Biomed Eng. 2014 Sep;42(9):1823-33. doi: 10.1007/s10439-014-1049-x. Epub 2014 Jun 24. Ann Biomed Eng. 2014. PMID: 24957635 Free PMC article.
-
High Speed Pneumatic Stepper Motor for MRI Applications.Ann Biomed Eng. 2019 Mar;47(3):826-835. doi: 10.1007/s10439-018-02174-0. Epub 2018 Dec 14. Ann Biomed Eng. 2019. PMID: 30552529
-
Design and Additive Manufacturing of a Continuous Servo Pneumatic Actuator.Micromachines (Basel). 2023 Aug 17;14(8):1622. doi: 10.3390/mi14081622. Micromachines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37630158 Free PMC article.
-
A New Type of Motor: Pneumatic Step Motor.IEEE ASME Trans Mechatron. 2007 Feb 1;12(1):98-106. doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2006.886258. IEEE ASME Trans Mechatron. 2007. PMID: 21528106 Free PMC article.
-
A 10-mm MR-Conditional Unidirectional Pneumatic Stepper Motor.IEEE ASME Trans Mechatron. 2015 Apr;20(2):782-788. doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2014.2305839. IEEE ASME Trans Mechatron. 2015. PMID: 25419104 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Open Source MR-Safe Pneumatic Radial Inflow Motor and Encoder (PRIME): Design and Manufacturing Guidelines.Int Symp Med Robot. 2023 Apr;2023:10.1109/ismr57123.2023.10130240. doi: 10.1109/ismr57123.2023.10130240. Epub 2023 May 25. Int Symp Med Robot. 2023. PMID: 38073863 Free PMC article.
-
Design and evaluation of a pneumatic actuation unit for a wasp-inspired self-propelled needle.PLoS One. 2024 Jul 2;19(7):e0306411. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0306411. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38954720 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling and Control of an MR-Safe Pneumatic Radial Inflow Motor and Encoder (PRIME).IEEE ASME Trans Mechatron. 2024 Jun;29(3):1714-1725. doi: 10.1109/tmech.2023.3329296. Epub 2023 Dec 13. IEEE ASME Trans Mechatron. 2024. PMID: 38895598 Free PMC article.
-
Computer-assisted planning for a concentric tube robotic system in neurosurgery.Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2019 Feb;14(2):335-344. doi: 10.1007/s11548-018-1890-8. Epub 2018 Nov 27. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2019. PMID: 30478533
-
Novel fabrication of soft microactuators with morphological computing using soft lithography.Microsyst Nanoeng. 2019 Sep 23;5:44. doi: 10.1038/s41378-019-0092-z. eCollection 2019. Microsyst Nanoeng. 2019. PMID: 31636933 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zemiti N, Bricault I, Fouard C, Sanchez B, and Cinquin P, “LPR: A CT and MR-Compatible Puncture Robot to Enhance Accuracy and Safety of Image-Guided Interventions,” IEEE/ASME Trans Mechatronics, 13(3):306–315, 2008.
-
- Van den Bosch MR, Moman MR, van Vulpen M, Battermann JJ, Duiveman E, van Schelven LJ, de Leeuw H, Lagendjik JJW, and Moerland MA, “MRI-guided robotic system for transperineal prostate interventions: proof of principle,” Phys Med Biol, 55:133–140, 2010. - PubMed
-
- Melzer A, Gutmann B, Remmele T, Wolf R, Lukoscheck A, Bock M, Bardenheuer H, and Fischer H, “Innomotion for Percutaneous Image-Guided Interventions: Principles and Evaluation of this MR- and CT-Compatible Robotic System,” IEEE Eng Med Biol Mag, pp. 66–73, May-Jun 2008. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
