Screening of Polyvalent Phage-Resistant Escherichia coli Strains Based on Phage Receptor Analysis
- PMID: 31105661
- PMCID: PMC6499177
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00850
Screening of Polyvalent Phage-Resistant Escherichia coli Strains Based on Phage Receptor Analysis
Abstract
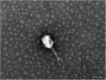
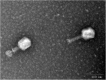
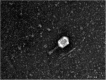
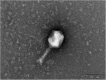
Bacteria-based biotechnology processes are constantly under threat from bacteriophage infection, with phage contamination being a non-neglectable problem for microbial fermentation. The essence of this problem is the complex co-evolutionary relationship between phages and bacteria. The development of phage control strategies requires further knowledge about phage-host interactions, while the widespread use of Escherichia coli strain BL21 (DE3) in biotechnological processes makes the study of phage receptors in this strain particularly important. Here, eight phages infecting E. coli BL21 (DE3) via different receptors were isolated and subsequently identified as members of the genera T4virus, Js98virus, Felix01virus, T1virus, and Rtpvirus. Phage receptors were identified by whole-genome sequencing of phage-resistant E. coli strains and sequence comparison with wild-type BL21 (DE3). Results showed that the receptors for the isolated phages, designated vB_EcoS_IME18, vB_EcoS_IME253, vB_EcoM_IME281, vB_EcoM_IME338, vB_EcoM_IME339, vB_EcoM_IME340, vB_EcoM_IME341, and vB_EcoS_IME347 were FhuA, FepA, OmpF, lipopolysaccharide, Tsx, OmpA, FadL, and YncD, respectively. A polyvalent phage-resistant BL21 (DE3)-derived strain, designated PR8, was then identified by screening with a phage cocktail consisting of the eight phages. Strain PR8 is resistant to 23 of 32 tested phages including Myoviridae and Siphoviridae phages. Strains BL21 (DE3) and PR8 showed similar expression levels of enhanced green fluorescent protein. Thus, PR8 may be used as a phage resistant strain for fermentation processes. The findings of this study contribute significantly to our knowledge of phage-host interactions and may help prevent phage contamination in fermentation.
Keywords: Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3); phage contamination; phage receptors; phage resistance; phage-host interaction.
Figures

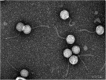
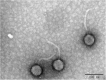
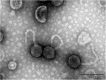
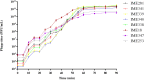

Similar articles
-
Complete Genome Sequences of Eight Phages Infecting Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in Swine.Microbiol Resour Announc. 2020 Sep 3;9(36):e00858-20. doi: 10.1128/MRA.00858-20. Microbiol Resour Announc. 2020. PMID: 32883794 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and Characterization of Dpo42, a Novel Depolymerase Derived from the Escherichia coli Phage vB_EcoM_ECOO78.Front Microbiol. 2017 Aug 2;8:1460. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01460. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28824588 Free PMC article.
-
vB_EcoS_IME347 a novel T1-like Escherichia coli bacteriophage.J Basic Microbiol. 2018 Nov;58(11):968-976. doi: 10.1002/jobm.201800271. Epub 2018 Aug 26. J Basic Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30146706
-
Characterization and Genomic Study of Phage vB_EcoS-B2 Infecting Multidrug-Resistant Escherichia coli.Front Microbiol. 2018 May 4;9:793. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00793. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29780362 Free PMC article.
-
Genome sequencing and analysis of an Escherichia coli phage vB_EcoM-ep3 with a novel lysin, Lysep3.Virus Genes. 2015 Jun;50(3):487-97. doi: 10.1007/s11262-015-1195-8. Epub 2015 Apr 5. Virus Genes. 2015. PMID: 25842152
Cited by
-
Bacteriophage-Insensitive Mutants of Antimicrobial-Resistant Salmonella Enterica are Altered in their Tetracycline Resistance and Virulence in Caco-2 Intestinal Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Mar 10;21(5):1883. doi: 10.3390/ijms21051883. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32164202 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization and Genomic Analysis of BUCT549, a Novel Bacteriophage Infecting Vibrio alginolyticus With Flagella as Receptor.Front Microbiol. 2021 Jun 17;12:668319. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.668319. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34220752 Free PMC article.
-
Phenotypic characterization and genomic analysis of Limosilactobacillus fermentum phage.Curr Res Food Sci. 2024 Apr 27;8:100748. doi: 10.1016/j.crfs.2024.100748. eCollection 2024. Curr Res Food Sci. 2024. PMID: 38764976 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization and complete genome sequence analysis of a newly isolatedphage against Vibrio parahaemolyticus from sick shrimp in Qingdao, China.PLoS One. 2022 May 4;17(5):e0266683. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0266683. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35507581 Free PMC article.
-
Precision targeting of genetic variations in mixed bacterial cultures using CRISPR-Cas12a-programmed λ phages.Front Microbiol. 2025 Jun 2;16:1575339. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1575339. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40529587 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Armstrong S. K., Francis C. L., Mcintosh M. A. (1990). Molecular analysis of the Escherichia coli ferric enterobactin receptor FepA. J. Biol. Chem. 265 14536–14543. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

