Notch-Mediated Tumor-Stroma-Inflammation Networks Promote Invasive Properties and CXCL8 Expression in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- PMID: 31105691
- PMCID: PMC6492532
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00804
Notch-Mediated Tumor-Stroma-Inflammation Networks Promote Invasive Properties and CXCL8 Expression in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Abstract
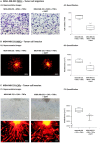
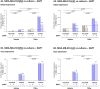
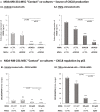
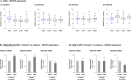
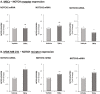
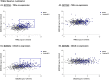
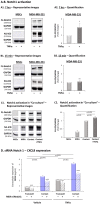
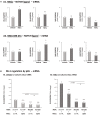
Stromal cells and pro-inflammatory cytokines play key roles in promoting the aggressiveness of triple-negative breast cancers (TNBC; Basal/Basal-like). In our previous study we demonstrated that stimulation of TNBC and mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) co-cultures by the pro-inflammatory cytokine tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα) has led to increased metastasis-related properties in vitro and in vivo. In this context, elevated release of the pro-metastatic chemokines CXCL8 (IL-8) and CCL5 (RANTES) was noted in TNFα- and interleukin-1β (IL-1β)-stimulated TNBC:MSC co-cultures; the process was partly (CXCL8) and entirely (CCL5) dependent on physical contacts between the two cell types. Here, we demonstrate that DAPT, inhibitor of γ-secretase that participates in activation of Notch receptors, inhibited the migration and invasion of TNBC cells that were grown in "Contact" co-cultures with MSCs or with patient-derived cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs), in the presence of TNFα. DAPT also inhibited the contact-dependent induction of CXCL8, but not of CCL5, in TNFα- and IL-1β-stimulated TNBC:MSC/CAF co-cultures; some level of heterogeneity between the responses of different TNBC cell lines was noted, with MDA-MB-231:MSC/CAF co-cultures being the most sensitive to DAPT. Patient dataset studies comparing basal tumors to luminal-A tumors, and mRNA analyses of Notch receptors in TNBC and luminal-A cells pointed at Notch1 as possible mediator of CXCL8 increase in TNFα-stimulated TNBC:stroma "Contact" co-cultures. Accordingly, down-regulation of Notch1 in TNBC cells by siRNA has substantially reduced the contact-dependent elevation in CXCL8 in TNFα- and also in IL-1β-stimulated TNBC:MSC "Contact" co-cultures. Then, studies in which CXCL8 or p65 (NF-κB pathway) were down-regulated (siRNAs; CRISPR/Cas9) in TNBC cells and/or MSCs, indicated that upon TNFα stimulation of "Contact" co-cultures, p65 was activated and led to CXCL8 production mainly in TNBC cells. Moreover, our findings indicated that when tumor cells interacted with stromal cells in the presence of pro-inflammatory stimuli, TNFα-induced p65 activation has led to elevated Notch1 expression and activation, which then gave rise to elevated production of CXCL8. Overall, tumor:stroma interactions set the stage for Notch1 activation by pro-inflammatory signals, leading to CXCL8 induction and consequently to pro-metastatic activities. These observations may have important clinical implications in designing novel therapy combinations in TNBC.
Keywords: CXCL8; cancer-associated fibroblasts; interleukin 1β; mesenchymal stem cells; notch1; p65; triple-negative breast cancer; tumor necrosis factor α.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Tumor-Stroma-Inflammation Networks Promote Pro-metastatic Chemokines and Aggressiveness Characteristics in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.Front Immunol. 2019 Apr 12;10:757. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00757. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31031757 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the inflammatory profile of stromal cells in human breast cancer: prominent roles for TNF-α and the NF-κB pathway.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015 May 1;6(1):87. doi: 10.1186/s13287-015-0080-7. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015. PMID: 25928089 Free PMC article.
-
Bruceine D suppresses CAF-promoted TNBC metastasis under TNF-α stimulation by inhibiting Notch1-Jagged1/NF-κB(p65) signaling.Phytomedicine. 2024 Jan;123:154928. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154928. Epub 2023 Jun 16. Phytomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38043386
-
Beyond Cell Motility: The Expanding Roles of Chemokines and Their Receptors in Malignancy.Front Immunol. 2020 Jun 4;11:952. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00952. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32582148 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glucocorticoid receptors orchestrate a convergence of host and cellular stress signals in triple negative breast cancer.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2024 Oct;243:106575. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2024.106575. Epub 2024 Jun 29. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38950871 Review.
Cited by
-
Notch Signaling in Breast Tumor Microenvironment as Mediator of Drug Resistance.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 4;23(11):6296. doi: 10.3390/ijms23116296. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35682974 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Crosstalk between Tumor-Infiltrating Immune Cells and Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts in Tumor Growth and Immunosuppression of Breast Cancer.J Immunol Res. 2021 Jul 13;2021:8840066. doi: 10.1155/2021/8840066. eCollection 2021. J Immunol Res. 2021. PMID: 34337083 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Understanding the functional inflammatory factors involved in therapeutic response to immune checkpoint inhibitors for pan-cancer.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 1;13:990445. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.990445. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36120342 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cancer associated fibroblast derived gene signature determines cancer subtypes and prognostic model construction in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas.Cancer Med. 2023 Mar;12(5):6388-6400. doi: 10.1002/cam4.5383. Epub 2022 Nov 20. Cancer Med. 2023. PMID: 36404634 Free PMC article.
-
A Robust Personalized Classification Method for Breast Cancer Metastasis Prediction.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Oct 29;14(21):5327. doi: 10.3390/cancers14215327. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36358745 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gerratana L, Fanotto V, Bonotto M, Bolzonello S, Andreetta C, Moroso S, et al. Pattern of metastatic spread and prognosis of breast cancer biologic subtypes. J Clin Oncol. (2014) 32:125–33. 10.1200/jco.2014.32.15_suppl.e12532 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

