The change tendency of endoplasmic reticulum stress associated proteins in rats with spinal cord injury
- PMID: 31105809
- PMCID: PMC6511803
The change tendency of endoplasmic reticulum stress associated proteins in rats with spinal cord injury
Abstract
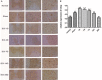
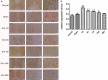
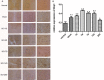
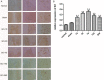
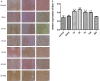
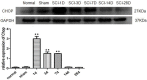
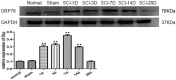
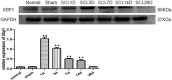
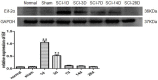
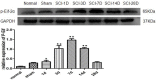
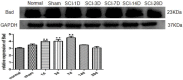
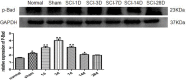
To investigate endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress reactions in spinal cord injury rats by evaluating the expression of the glucose-regulated protein 78 (GRP78), C/EBP homologous transcription factor protein (CHOP), X-box binding protein 1 (XBP1), Eif-2α and Bad. SCI models were established using adult female mice. After SCI, the expression of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis proteins were examined in the mice at specific time points using immunohistochemistry and western blot. The results of immunohistochemistry showed that in spinal cord gray matter, Chop, Grp78, XBP1, Eif-2α and Bad were specifically detected in the cytoplasm of the cell. Compare with the SCI group, there was little expression in normal group and sham group. The expression of ER stress-induced apoptosis proteins were significantly increased after spinal cord injury, and the absolute expression was higher than normal group (P < 0.05). Western-Blot results showed that compare with the SCI group, there were little expression of ER stress-induced apoptosis proteins in normal group and sham group. The expression of ER stress-induced apoptosis proteins were significantly increased after spinal cord injury, and the absolute expression was higher than normal group (P < 0.05). These results suggest that some ER stress-induced apoptosis proteins, such as Chop, Grp78, XBP1, Eif-2α and Bad, were activated after spinal cord injury, but the precise regulatory mechanisms remain unclear. In the future, understanding of the precise mechanism of ER stress-mediated apoptosis in SCI may lead to the development of novel treatment strategies.
Keywords: Chop; Eif-2α; Grp78; Spinal cord injury; endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Tian T, Yu Z, Zhang N, Chang Y, Zhang Y, Zhang L, Zhou S, Zhang C, Feng G, Huang F. Modified acellular nerve-delivering PMSCs improve functional recovery in rats after complete spinal cord transection. Biomater Sci. 2017;5:2480–2492. - PubMed
-
- Zhang Y, Hu H, Tian T, Zhang L, Zhao D, Wu Q, Chang Y, Wang Q, Zhou S, Feng G, Huang F. Mst3b promotes spinal cord neuronal regeneration by promoting growth cone branching out in spinal cord injury rats. Mol Neurobiol. 2015;51:1144–1157. - PubMed
-
- Wang J, Li H, Ren Y, Yao Y, Hu J, Zheng M, Ding Y, Chen YY, Shen Y, Wang LL, Zhu Y. Local delivery of beta-elemene improves locomotor functional recovery by alleviating endoplasmic reticulum stress and reducing neuronal apoptosis in rats with spinal cord injury. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;49:595–609. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
