MEF-2 isoforms' (A-D) roles in development and tumorigenesis
- PMID: 31105874
- PMCID: PMC6505634
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.26763
MEF-2 isoforms' (A-D) roles in development and tumorigenesis
Abstract
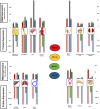
Myocyte enhancer factor (MEF)-2 plays a critical role in proliferation, differentiation, and development of various cell types in a tissue specific manner. Four isoforms of MEF-2 (A-D) differentially participate in controlling the cell fate during the developmental phases of cardiac, muscle, vascular, immune and skeletal systems. Through their associations with various cellular factors MEF-2 isoforms can trigger alterations in complex protein networks and modulate various stages of cellular differentiation, proliferation, survival and apoptosis. The role of the MEF-2 family of transcription factors in the development has been investigated in various cell types, and the evolving alterations in this family of transcription factors have resulted in a diverse and wide spectrum of disease phenotypes, ranging from cancer to infection. This review provides a comprehensive account on MEF-2 isoforms (A-D) from their respective localization, signaling, role in development and tumorigenesis as well as their association with histone deacetylases (HDACs), which can be exploited for therapeutic intervention.
Keywords: ATLL; HDACi; HDACs; HTLV-1; MEF-2.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Exercise and myocyte enhancer factor 2 regulation in human skeletal muscle.Diabetes. 2004 May;53(5):1208-14. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.53.5.1208. Diabetes. 2004. PMID: 15111488
-
Myocyte enhancer factor (MEF)-2 plays essential roles in T-cell transformation associated with HTLV-1 infection by stabilizing complex between Tax and CREB.Retrovirology. 2015 Feb 27;12:23. doi: 10.1186/s12977-015-0140-1. Retrovirology. 2015. PMID: 25809782 Free PMC article.
-
Oxytocin alters the morphology of hypothalamic neurons via the transcription factor myocyte enhancer factor 2A (MEF-2A).Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2018 Dec 5;477:156-162. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2018.06.013. Epub 2018 Jun 19. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2018. PMID: 29928931
-
Epigenetic regulation of skeletal muscle development and differentiation.Subcell Biochem. 2013;61:139-50. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-4525-4_7. Subcell Biochem. 2013. PMID: 23150250 Review.
-
Histone deacetylases in cardiac fibrosis: current perspectives for therapy.Cell Signal. 2014 Mar;26(3):521-7. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.11.037. Epub 2013 Dec 7. Cell Signal. 2014. PMID: 24321371 Review.
Cited by
-
Overexpressing lnc240 Rescues Learning and Memory Dysfunction in Hepatic Encephalopathy Through miR-1264-5p/MEF2C Axis.Mol Neurobiol. 2023 Apr;60(4):2277-2294. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03205-1. Epub 2023 Jan 16. Mol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 36645630
-
HDACs and Their Inhibitors on Post-Translational Modifications: The Regulation of Cardiovascular Disease.Cells. 2025 Jul 20;14(14):1116. doi: 10.3390/cells14141116. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40710369 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Three possible diagnostic biomarkers for gastric cancer: miR-362-3p, miR-362-5p and miR-363-5p.Biomark Med. 2024;18(10-12):567-579. doi: 10.1080/17520363.2024.2352419. Epub 2024 Jul 29. Biomark Med. 2024. PMID: 39072355 Free PMC article.
-
Novel perspectives on antisense transcription in HIV-1, HTLV-1, and HTLV-2.Front Microbiol. 2022 Dec 23;13:1042761. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1042761. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36620051 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 antisense promoter by myocyte enhancer factor-2C in the context of adult T-cell leukemia and lymphoma.Haematologica. 2022 Dec 1;107(12):2928-2943. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2021.279542. Haematologica. 2022. PMID: 35615924 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sacilotto N, Chouliaras KM, Nikitenko LL, Lu YW, Fritzsche M, Wallace MD, Nornes S, García-Moreno F, Payne S, Bridges E, Liu K, Biggs D, Ratnayaka I, et al. MEF2 transcription factors are key regulators of sprouting angiogenesis. Genes Dev. 2016;30:2297–309. doi: 10.1101/gad.290619.116. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

