Circular RNAs: an emerging landscape in tumor metastasis
- PMID: 31105992
- PMCID: PMC6511637
Circular RNAs: an emerging landscape in tumor metastasis
Abstract
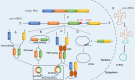
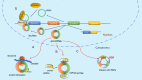
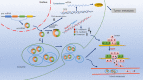
Circular RNAs (CircRNAs), the endogenous long noncoding RNAs, unlike linear RNAs, are structurally continuous, covalently closed loops without 5' cap or 3' polyadenylated tail. High-throughput RNA sequencing has enabled the discovery of several endogenous circRNAs in different species and tissues. The circRNAs mainly act as sponges to cytoplasmic microRNA, aid in protein translation, or interact with RNA-binding proteins to generate RNA-protein complexes which control transcription. Recently, circRNAs have been reported to participate in cancer pathogenesis, particularly tumor metastasis in humans, mainly due to their frequent aberrant expression in cancers. However, the detail molecular mechanism of circRNAs activity in tumor metastasis is still elusive. Some specifically expressed circRNAs can potentially be used as biomarkers and therapeutic targets for tumor treatment. Further understanding of the network interactions and regulation of circRNAs is paving the way for the identification of better therapeutic strategies in tumor metastasis. In this mini review, we have summarized the current state of research on functions and mechanisms of novel circRNAs that regulate tumorigenesis and have evaluated the relationship between dysregulation of circRNAs and tumor metastasis.
Keywords: Circular RNAs; DNA demethylation; back-splicing; epithelial-mesenchymal transition; exosomes; tumor metastasis.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Review on circular RNAs and new insights into their roles in cancer.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021 Jan 22;19:910-928. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2021.01.018. eCollection 2021. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021. PMID: 33598105 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomal circular RNAs: A new frontier in the metastasis of digestive system tumors.Oncol Lett. 2021 Dec;22(6):826. doi: 10.3892/ol.2021.13087. Epub 2021 Oct 12. Oncol Lett. 2021. PMID: 34691253 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circular RNAs: A novel type of biomarker and genetic tools in cancer.Oncotarget. 2017 Jun 2;8(38):64551-64563. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.18350. eCollection 2017 Sep 8. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28969093 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circular RNAs function as competing endogenous RNAs in multiple types of cancer.Oncol Lett. 2018 Jan;15(1):23-30. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.7348. Epub 2017 Nov 3. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 29387208 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNAs: Biogenesis, Function and Role in Human Diseases.Front Mol Biosci. 2017 Jun 6;4:38. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2017.00038. eCollection 2017. Front Mol Biosci. 2017. PMID: 28634583 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Automated One-Double-Z Pair BaseScope™ for CircRNA In Situ Hybridization.Methods Mol Biol. 2020;2148:379-388. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-0623-0_24. Methods Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 32394395
-
CircRNA hsa_circ_0070659 predicts poor prognosis and promotes non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) progression via microRNA-377 (miR-377) / Ras-Associated Binding Protein 3C (RAB3C) pathway.Bioengineered. 2022 Jun;13(6):14578-14594. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2091572. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 36694911 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma circN4BP2L2 is a promising novel diagnostic biomarker for epithelial ovarian cancer.BMC Cancer. 2022 Jan 3;22(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-09073-z. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 34980005 Free PMC article.
-
Novel circular RNA circSOBP governs amoeboid migration through the regulation of the miR-141-3p/MYPT1/p-MLC2 axis in prostate cancer.Clin Transl Med. 2021 Mar;11(3):e360. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.360. Clin Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 33784000 Free PMC article.
-
Doxorubicin inhibits osteosarcoma progression by regulating circ_0000006/miR-646/ BDNF axis.J Orthop Surg Res. 2021 Oct 30;16(1):645. doi: 10.1186/s13018-021-02782-y. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021. PMID: 34717683 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
