MiR-374b re-sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma cells to sorafenib therapy by antagonizing PKM2-mediated glycolysis pathway
- PMID: 31106002
- PMCID: PMC6511640
MiR-374b re-sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma cells to sorafenib therapy by antagonizing PKM2-mediated glycolysis pathway
Erratum in
-
Erratum: MiR-374b re-sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma cells to sorafenib therapy by antagonizing PKM2-mediated glycolysis pathway.Am J Cancer Res. 2025 Sep 25;15(9):4198-4199. doi: 10.62347/XRSE9244. eCollection 2025. Am J Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 41113983 Free PMC article.
Abstract
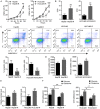
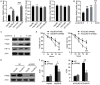
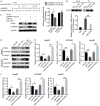
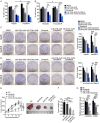
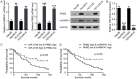
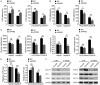
Despite impressively initial clinical responses, the majority of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients treated with sorafenib eventually develop resistance to this drug. It is well-known that microRNA (miRNA) plays a critical role in HCC progression and sorafenib resistance. However, the potential mechanism by which miRNA contributes to the human HCC cells to sorafenib resistance is still unknown. Herein, we identify miR-374b/hnRNPA1/PKM2 axis serving as an important mechanism for acquired sorafenib resistance of HCC cells. By establishing a sorafenib-resistant HCC model, we demonstrated that miR-374b reduces the expression of hnRNPA1 by binding to its 3' untranslated region, which subsequently decreases levels of PKM2. The suppression of PKM2 by miR-374b re-sensitizes sorafenib-resistant HCC cells and mouse xenografts to sorafenib treatment by antagonizing glycolysis pathway. Clinically, hnRNPA1 and PKM2 expression are upregulated and inversely associated with miR-374b expression level in sorafenib-resistant HCC patients. Moreover, sorafenib significantly induces the expression of hnRNPA1, which serves as an important mechanism for the acquired sorafenib resistance in HCCs. Thus, our data suggest that targeting the alternative splicing of the PKM by miR-374b overexpression may have significant implications in overcoming the resistance to sorafenib therapy.
Keywords: MiR-374b; PKM2; hepatocellular carcinoma; hnRNPA1; sorafenib.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Rimassa L, Abbadessa G, Personeni N, Porta C, Borbath I, Daniele B, Salvagni S, Van Laethem JL, Van Vlierberghe H, Trojan J. Tumor and circulating biomarkers in patients with second-line hepatocellular carcinoma from the randomized phase II study with tivantinib. Oncotarget. 2016;7:72622. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
