The impact of epidermal growth factor receptor mutations on the prognosis of resected non-small cell lung cancer: a meta-analysis of literatures
- PMID: 31106123
- PMCID: PMC6504652
- DOI: 10.21037/tlcr.2019.03.14
The impact of epidermal growth factor receptor mutations on the prognosis of resected non-small cell lung cancer: a meta-analysis of literatures
Abstract
Background: Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation represents a good response to EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitor and an advantageous prognostic factor in advanced-stage non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). However, the predictive value of EGFR mutation for prognosis in NSCLC patients after complete surgery, which more reflective of natural process, remains controversial. We sought to examine the predictive value of EGFR mutation in NSCLC. Several studies with small sample sizes have been reported but small studies bring bias especially in a postoperative setting. Therefore, we sought to pool all current evidence to show the true effects.
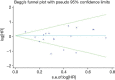
Methods: Electronic databases were used to search the relevant articles. Disease-free survival (DFS), which will be less effected by subsequent treatments after recurrence, was the primary endpoint. The DFS between EGFR mutated and wild-type patients were compared focus on stage I patients who are rarely received adjuvant therapy. Besides, the DFS of patients with 19 exon deletion (19del) and 21 exon L858R mutation (L858R) were compared. A random effects model was used.
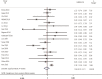
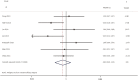
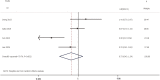
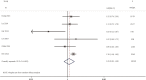
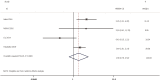
Results: A total of 19 relevant studies which involved 4,872 cases were enrolled and 2,086 patients were EGFR-mutated. The majority of studies used PCR-based methods to detect EGFR mutations. Through meta-analysis, we observed the DFS of EGFR-mutated patients were similar to wild type patients in overall population (HR 0.93, 95% CI: 0.74 to 1.17). Similar results were observed in stage I subgroup (HR 0.82, 95% CI: 0.50 to 1.33). DFS of 19 del patients were potentially inferior to L858R patients but the difference was not significant (HR 1.38, 95% CI: 0.76 to 2.52).
Conclusions: There was no significant difference in postoperative DFS between EGFR-mutant patients and wild-type with resected NSCLC. In addition, there is still insufficient evidence to support different postoperative treatment strategies (especially for stage I) for both mutated and wild-type patients. However, 19 del may be a negative factor, which may require more strict management. Thus, we strongly encourage reporting specific prognostic impacts of different mutation types.
Keywords: Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC); disease-free survival (DFS); epidermal growth factor receptor mutation (EGFR mutation); meta-analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures




Similar articles
-
EGFR inhibitors as adjuvant therapy for resected non-small cell lung cancer harboring EGFR mutations.Lung Cancer. 2019 Oct;136:6-14. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2019.08.001. Epub 2019 Aug 2. Lung Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31421260
-
Adjuvant EGFR-TKIs for Patients With Resected EGFR-Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Meta-Analysis of 1,283 Patients.Front Oncol. 2021 Apr 12;11:629394. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.629394. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33912453 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in the Adjuvant Setting for Patients with Resected Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Meta-Analysis with 11 Trials.Oncol Res Treat. 2021;44(6):344-353. doi: 10.1159/000515230. Epub 2021 May 5. Oncol Res Treat. 2021. PMID: 33951671
-
Efficacy and safety of adjuvant EGFR-TKIs for resected non-small cell lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis based on randomized control trials.BMC Cancer. 2022 Mar 26;22(1):328. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-09444-0. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35346117 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations from preoperative circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) as a prognostic predictor for stage I-III non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients with baseline tissue EGFR mutations.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2021 Jul;10(7):3213-3225. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-21-530. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 34430359 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
[Correlation Analysis of Ki67 Expression and EGFR Mutation on the Risk of Recurrence and Metastasis in Postoperative Patients with Stage I Lung Adenocarcinoma].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2022 Dec 20;25(12):852-861. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2022.101.55. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 36617471 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Prognostic factors in completely resected lymph-node-negative pulmonary adenocarcinoma.Transl Cancer Res. 2022 Jul;11(7):2238-2248. doi: 10.21037/tcr-21-2633. Transl Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35966323 Free PMC article.
-
Risk factors of postoperative recurrence and potential candidate of adjuvant radiotherapy in lung adenosquamous carcinoma.J Thorac Dis. 2020 Oct;12(10):5593-5602. doi: 10.21037/jtd-20-1979. J Thorac Dis. 2020. PMID: 33209392 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating immune checkpoint inhibitors and targeted therapies in the treatment of early stage non-small cell lung cancer: a narrative review.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2020 Dec;9(6):2656-2673. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-20-546. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 33489825 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive Comparison Between Adjuvant Targeted Therapy and Chemotherapy for EGFR-Mutant NSCLC Patients: A Cost-Effectiveness Analysis.Front Oncol. 2021 Mar 25;11:619376. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.619376. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33842322 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
