Is treatment with platelet-rich fibrin better than zinc oxide eugenol in cases of established dry socket for controlling pain, reducing inflammation, and improving wound healing?
- PMID: 31106135
- PMCID: PMC6502748
- DOI: 10.5125/jkaoms.2019.45.2.76
Is treatment with platelet-rich fibrin better than zinc oxide eugenol in cases of established dry socket for controlling pain, reducing inflammation, and improving wound healing?
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Is treatment with platelet-rich fibrin better than zinc oxide eugenol in cases of established dry socket for controlling pain, reducing inflammation, and improving wound healing?J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2019 Dec;45(6):377. doi: 10.5125/jkaoms.2019.45.6.377. Epub 2019 Dec 26. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2019. PMID: 31966985 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Objectives: To appraise the effectiveness of platelet-rich fibrin (PRF) in the management of established dry socket in terms of pain, inflammation, and wound healing.
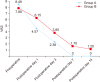
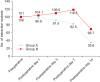
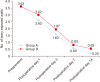
Materials and methods: Two hundred patients with established alveolar osteitis were studied to determine the efficacy of PRF and zinc oxide eugenol (ZOE) for pain control, inflammation reduction, and wound healing. Patients were randomly allocated to Group A (PRF) or Group B (ZOE). Patients were examined on the 1st, 3rd, 7th, and 14th postoperative day and evaluated for pain using visual analogue scale scores, inflammation with a gingival index score, and wound healing through a determination of the number of bony walls exposed.
Results: Group A showed better results in terms of pain remission, control of inflammation, and wound healing compared to Group B. Results between groups were statistically significant (P<0.05).
Conclusion: PRF is a better alternative than ZOE for the effective management of alveolar osteitis.
Keywords: Dry socket; Pain; Platelet-rich fibrin; Wound healing.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
References
-
- Bowe DC, Rogers S, Stassen LF. The management of dry socket/alveolar osteitis. J Ir Dent Assoc. 2011;57:305–310. - PubMed
-
- Crawford JY. Dry socket. Dent Cosms. 1896;38:929–931.
-
- Metin M, Tek M, Sener I. Comparison of two chlorhexidine rinse protocols on the incidence of alveolar osteitis following the surgical removal of impacted third molars. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2006;7:79–86. - PubMed
-
- Bloomer CR. Alveolar osteitis prevention by immediate placement of medicated packing. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2000;90:282–284. - PubMed
-
- Blum IR. Contemporary views on dry socket (alveolar osteitis): a clinical appraisal of standardization, aetiopathogenesis and management: a critical review. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2002;31:309–317. - PubMed

