Spine SBRT With Halcyon™: Plan Quality, Modulation Complexity, Delivery Accuracy, and Speed
- PMID: 31106151
- PMCID: PMC6498946
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00319
Spine SBRT With Halcyon™: Plan Quality, Modulation Complexity, Delivery Accuracy, and Speed
Abstract
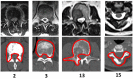
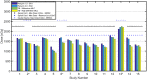
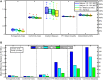
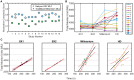
Purpose: Spine SBRT requires treatment plans with steep dose gradients and tight limits to the cord maximal dose. A new dual-layer staggered 1-cm MLC in Halcyon™ treatment platform has improved leakage, speed, and DLG compared to 120-Millennium (0.5-cm) and High-Definition (0.25-cm) MLCs in the TrueBeam platform. Halcyon™ 2.0 with SX2 MLC modulates fluence with the upper and lower MLCs, while in Halcyon™ 1.0 with SX1 only the lower MLC modulates the fluence and the upper MLC functions as a back-up jaw. We investigated the effects of four MLC designs on plan quality for spine SBRT treatments. Methods: 15 patients previously treated at our institution were re-planned according to the NRG-BR-002 guidelines with a prescription of 3,000 cGy in 3 fractions, 6xFFF, 800 MU/min, and 3-arc VMAT technique. Planning objectives were adjusted manually by an experienced planner to generate optimal plans and kept the same for different MLCs within the same platform. Results: All treatment plans were able to achieve adequate target coverage while meeting NRG-BR002 dosimetric constraints. Planning parameters were evaluated including: conformity index, homogeneity index, gradient measure, and global point dose maximum. Delivery accuracy, modulation complexity, and delivery time were also analyzed for all MLCs. Conclusion: The Halcyon™ dual-layer MLC can generate comparable and clinically equivalent spine SBRT plans to TrueBeam plans with less rapid dose fall-off and lower conformity. MLC width leaf can impact maximum dose to organs at risk and plan quality, but does not cause limitations in achieving acceptable plans for spine SBRT treatments.
Keywords: Halcyon™; SBRT; modulation complexity score; multi-leaf collimator; plan quality; spinal metastasis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of Multi-leaf Collimator Parameters on Head and Neck Plan Quality and Delivery: A Comparison between Halcyon™ and Truebeam® Treatment Delivery Systems.Cureus. 2018 Nov 28;10(11):e3648. doi: 10.7759/cureus.3648. Cureus. 2018. PMID: 30723647 Free PMC article.
-
Dosimetric evaluation and gradient analysis of various MLC leaf-width effects in external beam radiation therapy: TrueBeam Vs Halcyon.Radiography (Lond). 2024 Oct;30(6):1646-1654. doi: 10.1016/j.radi.2024.10.007. Epub 2024 Oct 21. Radiography (Lond). 2024. PMID: 39437610
-
Dosimetric effect of multileaf collimator leaf width on volumetric modulated arc stereotactic radiotherapy for spine tumors.Med Dosim. 2017 Summer;42(2):111-115. doi: 10.1016/j.meddos.2017.01.007. Epub 2017 Apr 28. Med Dosim. 2017. PMID: 28457723
-
Dosimetric Performance and Planning/Delivery Efficiency of a Dual-Layer Stacked and Staggered MLC on Treating Multiple Small Targets: A Planning Study Based on Single-Isocenter Multi-Target Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRS) to Brain Metastases.Front Oncol. 2019 Jan 22;9:7. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00007. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30723702 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of fluence-based dose delivery incorporating the spatial variation of dosimetric leaf gap (DLG).J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2016 Jan 8;17(1):12-21. doi: 10.1120/jacmp.v17i1.5883. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2016. PMID: 26894361 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Prostate Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy With Halcyon 2.0: Treatment Plans Comparison Based on RTOG 0938 Protocol.Cureus. 2020 Nov 23;12(11):e11660. doi: 10.7759/cureus.11660. Cureus. 2020. PMID: 33391899 Free PMC article.
-
Commissioning of Halcyon enhanced leaf model in the Eclipse treatment planning system: Focus on simple slit fields and VMAT dose calculation.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2025 Jun;26(6):e70044. doi: 10.1002/acm2.70044. Epub 2025 Feb 17. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2025. PMID: 39960336 Free PMC article.
-
Initial Clinical Experience Treating Patients With Gynecologic Cancers on a 6MV Flattening Filter Free O-Ring Linear Accelerator.Adv Radiat Oncol. 2020 Feb 8;5(5):920-928. doi: 10.1016/j.adro.2020.01.004. eCollection 2020 Sep-Oct. Adv Radiat Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33083654 Free PMC article.
-
Dosimetric Characterization of the Dual Layer MLC System for an O-Ring Linear Accelerator.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2019 Jan-Dec;18:1533033819883641. doi: 10.1177/1533033819883641. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2019. PMID: 31707918 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative dosimetric analysis of volumetric modulated arc therapy based craniospinal irradiation plans between Halcyon ring gantry and TrueBeam C-arm linear accelerator.Sci Rep. 2023 Mar 1;13(1):3430. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-30429-x. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36859485 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

