Endoscopic Brow Lift Fixation With Mitek Suture Anchors: A 9-Year Experience of a New "Ideal" Technique
- PMID: 31106165
- PMCID: PMC6505361
- DOI: 10.1177/2292550318800504
Endoscopic Brow Lift Fixation With Mitek Suture Anchors: A 9-Year Experience of a New "Ideal" Technique
Abstract
Purpose: In recent years, the endoscopic technique has emerged as a minimally invasive approach to forehead rejuvenation, although the specific need for and mode of brow fixation for endoscopic brow lifts remain under considerable debate. An ideal fixation device should provide non-palpable long-lasting fixation and allow retention of the device post-operatively without the need for removal. It should also allow precise intraoperative adjustment for symmetry and correction of brow ptosis.
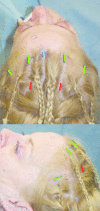
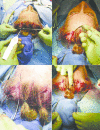
Methods: The authors describe an endoscopic brow lift technique using an absorbable bone anchor, Mitek Microfix. A retrospective chart review was conducted in patients who underwent endoscopic brow lift procedures utilizing this fixation method at an academic practice. Outcomes evaluated included operative times, reoperation rates, palpability, fixation device permanence, incremental costs comparisons to conventional methods, efficacy, and technical learning curve. Complication rates were evaluated and the economic, incremental cost analysis of current fixation methods was reviewed.
Results: Eighty-two patients underwent single-procedure endoscopic brow fixation using the Mitek anchor over a 9-year period (2005-2014). The mean operative time was 100 minutes. There were no cases of implant palpability, alopecia, or other postoperative complications. Two patients underwent revision secondary lifts after an average of 5.5 months for temporal ptosis.
Conclusion: The Mitek Microfix QuickAnchor provides durable, long-lasting fixation without device palpability. Its technical ease of use is demonstrated by the reasonable mean operative time achieved with the active involvement of resident surgeons. This device is operator-friendly, easy to use, fully indwelling, and provides lasting fixation without the development of palpability or alopecia.
Objectifs: Ces dernières années, la technique endoscopique est devenue une approche peu invasive du rajeunissement du front, mais la nécessité et le moyen de fixer les sourcils font l’objet de vifs débats. Le dispositif de fixation idéal doit être non palpable, durable et demeurer en place sans devoir être retiré. Il doit également assurer le rajustement intraopératoire précis de la symétrie et de la correction de la ptose des sourcils.
Méthodologie: Les auteurs décrivent une technique de redrapage endoscopique des sourcils à l’aide de l’ancre osseuse absorbable Mitek Microfix. Ils ont procédé à une analyse rétrospective des dossiers des patients qui avaient subi un redrapage endoscopique des sourcils à l’aide de cette méthode de fixation dans un cabinet universitaire. Ils ont évalué la durée de l’opération, le taux de réopérations, la palpabilité, la permanence du dispositif de fixation, les comparaisons des coûts différentiels par rapport aux méthodes traditionnelles, l’efficacité et la courbe d’apprentissage technique. Ils ont également évalué le taux de complications et examiné l’analyse des coûts différentiels des méthodes de fixation.
Résultats: Sur une période de neuf ans (de 2005 à 2014), 82 patients ont subi une seule intervention de fixation endoscopique des sourcils à l’aide de l’ancre Mitek. L’opération durait 100 minutes en moyenne. Il n’y a eu aucun cas de palpabilité de l’implant, d’alopécie ou d’autres complications postopératoires. Deux patients ont subi un redrapage secondaire après une ptose temporale au bout d’une période moyenne de 5,5 mois.
Conclusion: L’ancre Mitek Microfix QuickAnchor procure une fixation durable sans palpabilité du dispositif. La simplicité de la technique est démontrée par le temps moyen raisonnable de l’opération obtenu avec la participation active de résidents en chirurgie. Ce dispositif à demeure est facile à utiliser pour l’opérateur et procure une fixation durable sans apparition de palpabilité ou d’alopécie.
Keywords: Mitek suture anchor; brow fixation; brow lift; endoscopic brow lift.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting Interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Long-term Stability in Endoscopic Brow Lift: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Literature.Aesthet Surg J. 2025 Feb 18;45(3):232-240. doi: 10.1093/asj/sjae225. Aesthet Surg J. 2025. PMID: 39542644 Free PMC article.
-
Experience with cortical tunnel fixation in endoscopic brow lift: the "bevel and slide" modification.Int J Surg. 2009 Dec;7(6):510-5. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2009.08.013. Epub 2009 Oct 1. Int J Surg. 2009. PMID: 19800433 Review.
-
Suture fixation technique for endoscopic brow lift.Semin Plast Surg. 2008 Feb;22(1):43-9. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1019142. Semin Plast Surg. 2008. PMID: 20567688 Free PMC article.
-
Secondary endoscopic forehead lift in patients with previous coronal brow lifts.Ann Plast Surg. 2005 Mar;54(3):251-5. Ann Plast Surg. 2005. PMID: 15725825
-
Endoscopic brow lift: a retrospective review of 628 consecutive cases over 5 years.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2003 Aug;112(2):628-33; discussion 634-5. doi: 10.1097/01.PRS.0000071042.11435.2E. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2003. PMID: 12900626
Cited by
-
Evaluation and treatment of facial feminization surgery: part I. forehead, orbits, eyebrows, eyes, and nose.Arch Plast Surg. 2021 Sep;48(5):503-510. doi: 10.5999/aps.2021.00199. Epub 2021 Sep 15. Arch Plast Surg. 2021. PMID: 34583435 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term Stability in Endoscopic Brow Lift: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Literature.Aesthet Surg J. 2025 Feb 18;45(3):232-240. doi: 10.1093/asj/sjae225. Aesthet Surg J. 2025. PMID: 39542644 Free PMC article.
-
Fixation Techniques Across Endoscopic Brow Lifts: A Scoping Review.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2025 Aug 13. doi: 10.1007/s00266-025-05114-1. Online ahead of print. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2025. PMID: 40804547 Review.
References
-
- Passot R. La chirurgie esthetique des rides du visage. Presse Med. 1919;27:258–260.
-
- Gonzalez-Ulloa M. Facial wrinkles. Integral elimination. Plast Reconstr Surg Transplant Bull. 1962;29:658–673. - PubMed
-
- Vasconez LO, Core GB, Gamboa-Bobadilla M, Guzman G, Askren C, Yamamoto Y. Endoscopic techniques in coronal brow lifting. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1994;94(6):788–793. - PubMed
-
- Isse NG. Endoscopic facial rejuvenation: endoforehead, the functional lift. Case reports. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 1994;18(1):21–29. - PubMed
-
- Isse NG. Endoscopic forehead lift. Evolution and update. Clin Plast Surg. 1995;22(4):661–673. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
